Concept of an artificial muscle design on polypyrrole nanofiber scaffolds
- PMID: 32392238
- PMCID: PMC7213722
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232851
Concept of an artificial muscle design on polypyrrole nanofiber scaffolds
Abstract
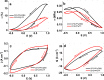
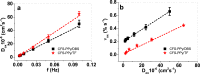
Here we present the synthesis and characterization of two new conducting materials having a high electro-chemo-mechanical activity for possible applications as artificial muscles or soft smart actuators in biomimetic structures. Glucose-gelatin nanofiber scaffolds (CFS) were coated with polypyrrole (PPy) first by chemical polymerization followed by electrochemical polymerization doped with dodecylbenzensulfonate (DBS-) forming CFS-PPy/DBS films, or with trifluoromethanesulfonate (CF3SO3-, TF) giving CFS-PPy/TF films. The composition, electronic and ionic conductivity of the materials were determined using different techniques. The electro-chemo-mechanical characterization of the films was carried out by cyclic voltammetry and square wave potential steps in bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonimide lithium solutions of propylene carbonate (LiTFSI-PC). Linear actuation of the CFS-PPy/DBS material exhibited 20% of strain variation with a stress of 0.14 MPa, rather similar to skeletal muscles. After 1000 cycles, the creeping effect was as low as 0,2% having a good long-term stability showing a strain variation per cycle of -1.8% (after 1000 cycles). Those material properties are excellent for future technological applications as artificial muscles, batteries, smart membranes, and so on.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Baughman RH. Conducting polymer artificial muscles. Synth Met. 1996;78: 339–353. 10.1016/0379-6779(96)80158-5 - DOI
-
- Melling D, Martinez JG, Jager EWH. Conjugated Polymer Actuators and Devices: Progress and Opportunities. Adv Mater. 2019;31: 1808210. - PubMed
-
- Hara S, Zama T, Takashima W, Kaneto K. TFSI-doped polypyrrole actuator with 26% strain. J Mater Chem. 2004;14: 1516 10.1039/b404232h - DOI
-
- Hara S, Zama T, Tanaka N, Takashima W, Kaneto K. Artificial fibular muscles with 20% strain based on polypyrrole-metal coil composites. Chem Lett. 2005;34: 784–785. 10.1246/cl.2005.784 - DOI
-
- Aziz S, Spinks GM. Torsional artificial muscles. Mater Horizons. 2020; accepted. 10.1039/c9mh01441a - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

