Inflammatory Type 2 cDCs Acquire Features of cDC1s and Macrophages to Orchestrate Immunity to Respiratory Virus Infection
- PMID: 32392463
- PMCID: PMC7207120
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.04.005
Inflammatory Type 2 cDCs Acquire Features of cDC1s and Macrophages to Orchestrate Immunity to Respiratory Virus Infection
Abstract
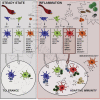
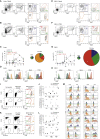
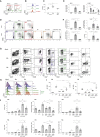
The phenotypic and functional dichotomy between IRF8+ type 1 and IRF4+ type 2 conventional dendritic cells (cDC1s and cDC2s, respectively) is well accepted; it is unknown how robust this dichotomy is under inflammatory conditions, when additionally monocyte-derived cells (MCs) become competent antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Using single-cell technologies in models of respiratory viral infection, we found that lung cDC2s acquired expression of the Fc receptor CD64 shared with MCs and of IRF8 shared with cDC1s. These inflammatory cDC2s (inf-cDC2s) were superior in inducing CD4+ T helper (Th) cell polarization while simultaneously presenting antigen to CD8+ T cells. When carefully separated from inf-cDC2s, MCs lacked APC function. Inf-cDC2s matured in response to cell-intrinsic Toll-like receptor and type 1 interferon receptor signaling, upregulated an IRF8-dependent maturation module, and acquired antigens via convalescent serum and Fc receptors. Because hybrid inf-cDC2s are easily confused with monocyte-derived cells, their existence could explain why APC functions have been attributed to MCs.
Keywords: CD64; Fc receptor; IRF8; convalescent serum; dendritic cell; inf-cDC2; inflammation; monocyte; transcription factor; type 1 interferon; virus.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Case of mistaken identity.Nat Rev Immunol. 2020 Jul;20(7):408-409. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0363-9. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32514033 No abstract available.
-
Where's Waldo: Identifying DCs within Mononuclear Phagocytes during Inflammation.Immunity. 2020 Jun 16;52(6):892-894. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.05.006. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 32553175
-
A recently described type 2 conventional dendritic cell (cDC2) subset mediates inflammation.Cell Mol Immunol. 2020 Dec;17(12):1215-1217. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0511-y. Epub 2020 Jul 30. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32732988 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bain C.C., Scott C.L., Uronen-Hansson H., Gudjonsson S., Jansson O., Grip O., Guilliams M., Malissen B., Agace W.W., Mowat A.M. Resident and pro-inflammatory macrophages in the colon represent alternative context-dependent fates of the same Ly6Chi monocyte precursors. Mucosal Immunol. 2013;6:498–510. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

