Dysregulation of Rho GTPases in Human Cancers
- PMID: 32392742
- PMCID: PMC7281333
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12051179
Dysregulation of Rho GTPases in Human Cancers
Abstract
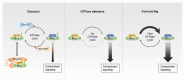
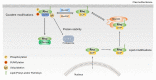
Rho GTPases play central roles in numerous cellular processes, including cell motility, cell polarity, and cell cycle progression, by regulating actin cytoskeletal dynamics and cell adhesion. Dysregulation of Rho GTPase signaling is observed in a broad range of human cancers, and is associated with cancer development and malignant phenotypes, including metastasis and chemoresistance. Rho GTPase activity is precisely controlled by guanine nucleotide exchange factors, GTPase-activating proteins, and guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors. Recent evidence demonstrates that it is also regulated by post-translational modifications, such as phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and sumoylation. Here, we review the current knowledge on the role of Rho GTPases, and the precise mechanisms controlling their activity in the regulation of cancer progression. In addition, we discuss targeting strategies for the development of new drugs to improve cancer therapy.
Keywords: Rho GTPases; cancer; chemoresistance; metastasis; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

