Berberine attenuates fructose-induced insulin resistance by stimulating the hepatic LKB1/AMPK/PGC1α pathway in mice
- PMID: 32393087
- PMCID: PMC7269079
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2020.1756349
Berberine attenuates fructose-induced insulin resistance by stimulating the hepatic LKB1/AMPK/PGC1α pathway in mice
Abstract
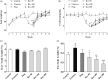
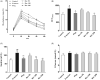
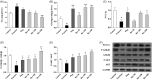
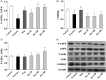
Context: Berberine is an alkaloid that possesses various pharmacologic effects.Objective: To explore the mechanism of berberine to improve insulin sensitivity in fructose-fed mice.Materials and methods: Sixty male ICR mice were randomly divided into 6 groups (10 mice in each group): control, fructose, pioglitazone (10 mg/kg) and berberine (50, 100, and 200 mg/kg). Except for the control group, the mice received 20% fructose drinking for 10 weeks. Pioglitazone and berberine were orally administered once daily during the last 4 weeks. The insulin sensitivity was evaluated using an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). The serum levels of fasting glucose and insulin, blood lipids, and hormones were determined. The hepatic AMP and ATP contents were detected using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis, and the protein expression was examined by immunoblotting.Results: Berberine significantly reversed the insulin resistance induced by fructose, including lowering fasting insulin levels (from 113.9 to 67.4) and area under the curve (AUC) during OGTT (from 1310 to 1073), decreasing serum leptin (from 0.28 to 0.13) and increasing serum adiponectin levels (from 1.50 to 2.80). Moreover, berberine enhanced the phosphorylation levels of protein kinase B (PKB/AKT; 2.27-fold) and glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β; 2.56-fold), and increased hepatic glycogen content (from 0.19 to 1.65). Furthermore, berberine upregulated the protein expression of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma coactivator 1α (PGC1α; 2.61-fold), phospho-AMP-activated protein kinase (p-AMPK; 1.35-fold) and phospho-liver kinase B1 (p-LKB1; 1.41-fold), whereas it decreased the AMP/ATP ratio (from 4.25 to 1.82).Conclusion: The present study demonstrated the protective effects of berberine against insulin resistance induced by fructose. Our findings may provide an experimental basis for the application of berberine in the treatment of insulin resistance.
Keywords: Insulin sensitivity; alkaloid; metabolic homeostasis; signalling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Bajaj M, Suraamornkul S, Pratipanawatr T, Hardies LJ, Pratipanawatr W, Glass L, Cersosimo E, Miyazaki Y, DeFronzo RA.. 2003. Pioglitazone reduces hepatic fat content and augments splanchnic glucose uptake in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 52:1364–1370. - PubMed
-
- Besse-Patin A, Leveille M, Oropeza D, Nguyen BN, Prat A, Estall JL.. 2017. Estrogen signals through peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α to reduce oxidative damage associated with diet-induced fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 152:243–256. - PubMed
-
- Bursac BN, Vasiljevic AD, Nestorovic NM, Velickovic NA, Vojnovic Milutinovic DD, Matic GM, Djordjevic AD.. 2014. High-fructose diet leads to visceral adiposity and hypothalamic leptin resistance in male rats–do glucocorticoids play a role? J Nutr Biochem. 25:446–455. - PubMed
-
- Carling D. 2004. The AMP-activated protein kinase cascade–a unifying system for energy control. Trends Biochem Sci. 29:18–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
