Outpatient Otolaryngology in the Era of COVID-19: A Data-Driven Analysis of Practice Patterns
- PMID: 32393101
- PMCID: PMC7218354
- DOI: 10.1177/0194599820928987
Outpatient Otolaryngology in the Era of COVID-19: A Data-Driven Analysis of Practice Patterns
Abstract
Introduction: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has induced a prioritization of acute care and telehealth, affecting the quantity of patients seen and the modality of their care.
Study design: Retrospective review.
Setting: Single-institution study conducted within the Division of Otolaryngology at the Yale School of Medicine.
Subjects and methods: Data on all outpatient appointments within the Division of Otolaryngology were obtained from administrative records of billing and scheduling from March 16 to April 10, 2020. For comparison, a corresponding period from 2019 was also utilized.
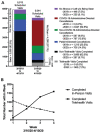
Results: Of 5913 scheduled visits, 3665 (62.0%) were seen between March 18 and April 12, 2019, in comparison with 649 of 5044 (12.9%) during the corresponding COVID-19-affected period. The majority of completed visits performed in weeks 1 and 2 were in person, while the majority in weeks 3 and 4 were via telehealth. Among subspecialties, a larger proportion of completed visits in 2020 were performed by pediatric and head and neck oncology otolaryngologists as compared with general/specialty otolaryngologists (P < .001). Older adults (≥65 years) were less likely to have telehealth visits than younger adults (18-64 years; 45.6% vs 59.6%, P = .003).
Conclusions: A major decrease in the completion rates of scheduled visits was seen in the COVID-19-affected period, though this was not proportional among subspecialties. An associated increase in telehealth visits was observed. After COVID-19-related hospital policy changes, approximately 2 weeks passed before telehealth visits surpassed in-person visits, though this was not true among older adults.
Keywords: COVID-19; finances; health care; otolaryngology; telehealth.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization. Statement on the Second Meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee Regarding the Outbreak of Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). World Health Organization; 2020.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

