Association of the insulin resistance marker TyG index with the severity and mortality of COVID-19
- PMID: 32393351
- PMCID: PMC7213552
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-020-01035-2
Association of the insulin resistance marker TyG index with the severity and mortality of COVID-19
Abstract
Background: The triglyceride and glucose index (TyG) has been proposed as a marker of insulin resistance. This study aims to evaluate the association of the TyG index with the severity and mortality of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Methods: The study included a cohort of 151 patients with COVID-19 admitted in a tertiary teaching hospital in Wuhan. Regression models were used to investigate the association between TyG with severity and mortality of COVID-19.
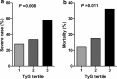
Results: In this cohort, 39 (25.8%) patients had diabetes, 62 (41.1%) patients were severe cases, while 33 (22.0%) patients died in hospital. The TyG index levels were significantly higher in the severe cases and death group (mild vs. severe 8.7 ± 0.6 vs. 9.2 ± 0.6, P < 0.001; survivor vs. deceased 8.8 ± 0.6 vs. 9.3 ± 0.7, P < 0.001), respectively. The TyG index was significantly associated with an increased risk of severe case and mortality, after controlling for potential confounders (OR for severe case, 2.9, 95% CI 1.2-6.3, P = 0.007; OR for mortality, 2.9, 95% CI 1.2-6.7, P = 0.016). The associations were not statistically significant for further adjustment of inflammatory factors.
Conclusion: TyG index was closely associated with the severity and morbidity in COVID-19 patients, thus it may be a valuable marker for identifying poor outcome of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Mortality; Severity; TyG index.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Summary of probable SARS cases with onset of illness from 1 November 2002 to 31 July 2003. 2003. https://www.who.int/csr/sars/country/table.2004_04_21/en/ Accessed 29 Feb 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical