Comparing the effects of ketorolac and Paracetamol on postoperative pain relief after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. A randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 32393370
- PMCID: PMC7216617
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-020-01125-y
Comparing the effects of ketorolac and Paracetamol on postoperative pain relief after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. A randomized clinical trial
Erratum in
-
Correction: Comparing the effects of ketorolac and Paracetamol on postoperative pain relief after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. a randomized clinical trial.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025 Aug 2;20(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s13019-025-03524-5. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025. PMID: 40753250 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Introduction: Pain management after coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery remains challenging.
Objective: This study aimed to compare the effects of Ketorolac and Paracetamol on postoperative CABG pain relief.
Method: This double-blind randomized clinical trial study was conducted in Ahvaz, Iran, from September 2018-December 2019. Two consecutive groups of 60 patients undergoing elective on-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery.
Intervention: The patients were divided into 0.5 mg/kg of ketorolac mg/dl and 10 mg/kg of Paracetamol after surgery for pain management. Primary outcomes were: visual analog pain scale (VAS) at the time point immediately after extubation (baseline) and at 6, 12, 24 and 48 h and the total dose of morphine consumption. Secondary outcomes included the hemodynamic variables, weaning time, chest tube derange, in-hospital mortality and myocardial infarction.
Statistical analysis: The data were analyzed using SPSS version 22(SPSS, Chicago, IL). The Mann-Whitney U-test was used to compare demographic data, VAS scores, vital signs, and side effects. Repeated measurements were tested within groups using Friedman's ANOVA and the Wilcoxon rank-sum test. Values were expressed as means ± standard deviations. Statistical significance was defined as a p-value < 0.05.
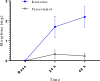
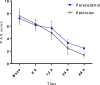
Results: Compared with baseline scores, there were significant declines in VAS scores in both groups throughout the time sequence (P< 0.05). The statistical VAS score was slightly higher in the Paracetamol group at most time points, except for the time of 6 h. However, at 24 and 48 h, the VAS score in group Paracetamol was significantly higher than in group Ketorolac. There were no significant differences between groups about hemodynamic variables.
Conclusion: The efficacy of ketorolac is comparable to that of Paracetamol in postoperative CABG pain relief.
Trial registry: IRCT20150216021098N5. Registered at 2019-09-12.
Keywords: Cardiac surgery; Ketorolac; Paracetamol; Postoperative analgesia; Visual analog score.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Apfelbaum JL, Chen C, Mehta SS, Gan TJ. Postoperative pain experience: results from a national survey suggest postoperative pain continues to be undermanaged. Anesth Analg. 2003;97(2):534–40. - PubMed
-
- Brennan F, Carr DB, Cousins M. Pain management: a fundamental human right. Anesth Analg. 2007;105(1):205–21. - PubMed
-
- Liu SS, Block BM, Wu CL. Effects of perioperative central neuraxial analgesia on outcome after coronary artery bypass surgery—a meta-analysis. Anesthesiology. 2004;101(1):153–61. - PubMed
-
- Bainbridge D, Martin JE, Cheng DC. Patient-controlledversus nurse-controlled analgesia after cardiac surgery—a meta-analysis. Can J Anesth. 2006;53(5):492. - PubMed
-
- Ucak A, Onan B, Sen H, Selcuk I, Turan A, Yilmaz ATJJ. Anesthesia v: The effects of gabapentin on acute and chronic postoperative pain after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2011;25(5):824–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical