The PDK1-FoxO1 signaling in adipocytes controls systemic insulin sensitivity through the 5-lipoxygenase-leukotriene B4 axis
- PMID: 32393635
- PMCID: PMC7261087
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1921015117
The PDK1-FoxO1 signaling in adipocytes controls systemic insulin sensitivity through the 5-lipoxygenase-leukotriene B4 axis
Abstract
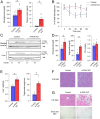
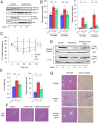
Although adipocytes are major targets of insulin, the influence of impaired insulin action in adipocytes on metabolic homeostasis remains unclear. We here show that adipocyte-specific PDK1 (3'-phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1)-deficient (A-PDK1KO) mice manifest impaired metabolic actions of insulin in adipose tissue and reduction of adipose tissue mass. A-PDK1KO mice developed insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, and hepatic steatosis, and this phenotype was suppressed by additional ablation of FoxO1 specifically in adipocytes (A-PDK1/FoxO1KO mice) without an effect on adipose tissue mass. Neither circulating levels of adiponectin and leptin nor inflammatory markers in adipose tissue differed between A-PDK1KO and A-PDK1/FoxO1KO mice. Lipidomics and microarray analyses revealed that leukotriene B4 (LTB4) levels in plasma and in adipose tissue as well as the expression of 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) in adipose tissue were increased and restored in A-PDK1KO mice and A-PDK1/FoxO1KO mice, respectively. Genetic deletion of the LTB4 receptor BLT1 as well as pharmacological intervention to 5-LO or BLT1 ameliorated insulin resistance in A-PDK1KO mice. Furthermore, insulin was found to inhibit LTB4 production through down-regulation of 5-LO expression via the PDK1-FoxO1 pathway in isolated adipocytes. Our results indicate that insulin signaling in adipocytes negatively regulates the production of LTB4 via the PDK1-FoxO1 pathway and thereby maintains systemic insulin sensitivity.
Keywords: 5-lipoxygenase; FoxO1; PDK1; insulin resistance; leukotriene B4.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures




References
-
- Giorgino F., Laviola L., Eriksson J. W., Regional differences of insulin action in adipose tissue: Insights from in vivo and in vitro studies. Acta Physiol. Scand. 183, 13–30 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Fasshauer M., Paschke R., Regulation of adipocytokines and insulin resistance. Diabetologia 46, 1594–1603 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Fève B., Adipogenesis: Cellular and molecular aspects. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 19, 483–499 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Blüher M., et al. , Adipose tissue selective insulin receptor knockout protects against obesity and obesity-related glucose intolerance. Dev. Cell 3, 25–38 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

