Restoring synovial homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes
- PMID: 32393826
- PMCID: PMC7987137
- DOI: 10.1038/s41584-020-0413-5
Restoring synovial homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes
Abstract
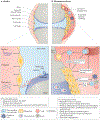
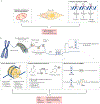
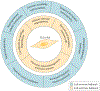
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic immune-mediated disease that primarily affects the synovium of diarthrodial joints. During the course of RA, the synovium transforms into a hyperplastic invasive tissue that causes destruction of cartilage and bone. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS), which form the lining of the joint, are epigenetically imprinted with an aggressive phenotype in RA and have an important role in these pathological processes. In addition to producing the extracellular matrix and joint lubricants, FLS in RA produce pathogenic mediators such as cytokines and proteases that contribute to disease pathogenesis and perpetuation. The development of multi-omics integrative analyses have enabled new ways to dissect the mechanisms that imprint FLS, have helped to identify potential FLS subsets with distinct functions and have identified differences in FLS phenotypes between joints in individual patients. This Review provides an overview of advances in understanding of FLS biology and highlights omics approaches and studies that hold promise for identifying future therapeutic targets.
Figures

References
-
- Klareskog L, Catrina AI & Paget S Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 373, 659–672 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Arnett FC et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 31, 315–324 (1988). - PubMed
-
- Choy EH, Kavanaugh AF & Jones SA The problem of choice: current biologic agents and future prospects in RA. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol 9, 154–163 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

