The emerging roles of WBP2 oncogene in human cancers
- PMID: 32393834
- PMCID: PMC7286818
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-020-1318-0
The emerging roles of WBP2 oncogene in human cancers
Abstract
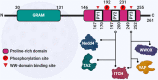
WW domain-binding protein 2 (WBP2) is an emerging oncoprotein. Over the past decade, WBP2 surfaced as a key node connecting key signaling pathways associated with ER/PR, EGFR, PI3K, Hippo, and Wnt in cancer. In addition to the oncogenic functions of WBP2, this review discusses the latest research regarding the multilevel regulation and modes of action of WBP2 and how they can be exploited for molecular medicine. In translational research, evidence supports the role of WBP2 as a biomarker for early detection, prognosis, and companion diagnostics in breast cancer. Finally, we envision new trends in WBP2 research in the space of molecular etiology of cancer, targeted therapeutics, and precision medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Buffa L, Saeed AM, Nawaz Z. Molecular mechanism of WW‐domain binding protein‐2 coactivation function in estrogen receptor signaling. IUBMB Life. 2013;65:76–84. - PubMed
-
- Dhananjayan SC, Ramamoorthy S, Khan OY, Ismail A, Sun J, Slingerland J, et al. WW domain binding protein-2, an E6-associated protein interacting protein, acts as a coactivator of estrogen and progesterone receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20:2343–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

