Uncoupling histone H3K4 trimethylation from developmental gene expression via an equilibrium of COMPASS, Polycomb and DNA methylation
- PMID: 32393859
- PMCID: PMC7790509
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-020-0618-1
Uncoupling histone H3K4 trimethylation from developmental gene expression via an equilibrium of COMPASS, Polycomb and DNA methylation
Abstract
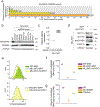
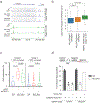
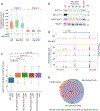
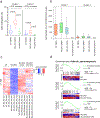
The COMPASS protein family catalyzes histone H3 Lys 4 (H3K4) methylation and its members are essential for regulating gene expression. MLL2/COMPASS methylates H3K4 on many developmental genes and bivalent clusters. To understand MLL2-dependent transcriptional regulation, we performed a CRISPR-based screen with an MLL2-dependent gene as a reporter in mouse embryonic stem cells. We found that MLL2 functions in gene expression by protecting developmental genes from repression via repelling PRC2 and DNA methylation machineries. Accordingly, repression in the absence of MLL2 is relieved by inhibition of PRC2 and DNA methyltransferases. Furthermore, DNA demethylation on such loci leads to reactivation of MLL2-dependent genes not only by removing DNA methylation but also by opening up previously CpG methylated regions for PRC2 recruitment, diluting PRC2 at Polycomb-repressed genes. These findings reveal how the context and function of these three epigenetic modifiers of chromatin can orchestrate transcriptional decisions and demonstrate that prevention of active repression by the context of the enzyme and not H3K4 trimethylation underlies transcriptional regulation on MLL2/COMPASS targets.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures










References
-
- Kouzarides T Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 128, 693–705 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Meeks JJ & Shilatifard A Multiple Roles for the MLL/COMPASS Family in the Epigenetic Regulation of Gene Expression and in Cancer. Annual Review of Cancer Biology 1, 425–446 (2017).
-
- Schneider J et al. Molecular regulation of histone H3 trimethylation by COMPASS and the regulation of gene expression. Mol Cell 19, 849–56 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

