Thenar oxygen saturation (StO2) alterations during a spontaneous breathing trial predict extubation failure
- PMID: 32394211
- PMCID: PMC7214564
- DOI: 10.1186/s13613-020-00670-y
Thenar oxygen saturation (StO2) alterations during a spontaneous breathing trial predict extubation failure
Abstract
Background: Weaning from mechanical ventilation (MV) is a cardiovascular stress test. Monitoring the regional oxygenation status has shown promising results in predicting the tolerance to spontaneously breathe in the process of weaning from MV. Our aim was to determine whether changes in skeletal muscle oxygen saturation (StO2) measured by near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) on the thenar eminence during a vascular occlusion test (VOT) can be used to predict extubation failure from mechanical ventilation.
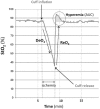
Methods: We prospectively studied 206 adult patients with acute respiratory failure receiving MV for at least 48 h from a 30-bed mixed ICU, who were deemed ready to wean by their physicians. Patients underwent a 30-min spontaneous breathing trial (SBT), and were extubated according to the local protocol. Continuous StO2 was measured non-invasively on the thenar eminence. A VOT was performed prior to and at 30 min of the SBT (SBT30). The rate of StO2 deoxygenation (DeO2), StO2 reoxygenation (ReO2) rate and StO2 hyperemic response to ischemia (HAUC) were calculated.
Results: Thirty-six of the 206 patients (17%) failed their SBT. The remainder 170 patients (83%) were extubated. Twenty-three of these patients (13.5%) needed reinstitution of MV within 24 h. Reintubated patients displayed a lower HAUC at baseline, and higher relative changes in their StO2 deoxygenation rate between baseline and SBT30 (DeO2 Ratio). A logistic regression-derived StO2 score, combining baseline StO2, HAUC and DeO2 ratio, showed an AUC of 0.84 (95% CI 0.74-0.91) for prediction of extubation failure.
Conclusions: Extubation failure was associated to baseline and dynamic StO2 alterations during the SBT. Monitoring StO2-derived parameters might be useful in predicting extubation outcome.
Keywords: Mechanical ventilation; Microcirculation; Near-infrared spectroscopy; Regional blood flow; Tissue oxygenation; Weaning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peripheral microcirculatory alterations are associated with the severity of acute respiratory distress syndrome in COVID-19 patients admitted to intermediate respiratory and intensive care units.Crit Care. 2021 Nov 8;25(1):381. doi: 10.1186/s13054-021-03803-2. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 34749792 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Characterization of tissue oxygen saturation and the vascular occlusion test: influence of measurement sites, probe sizes and deflation thresholds.Crit Care. 2009;13 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):S3. doi: 10.1186/cc8001. Epub 2009 Nov 30. Crit Care. 2009. PMID: 19951387 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in thenar muscle tissue oxygen saturation assessed by near-infrared spectroscopy during weaning from mechanical ventilation.Minerva Anestesiol. 2014 Jun;80(6):666-75. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Minerva Anestesiol. 2014. PMID: 24226488
-
Thenar Muscle Oxygen Saturation Using Vascular Occlusion Test: A Novel Technique to Study Microcirculatory Abnormalities in Pediatric Heart Failure Patients.Pediatr Cardiol. 2019 Aug;40(6):1151-1158. doi: 10.1007/s00246-019-02118-y. Epub 2019 May 16. Pediatr Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31098675 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal muscle oxygen saturation (StO2) measured by near-infrared spectroscopy in the critically ill patients.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:502194. doi: 10.1155/2013/502194. Epub 2013 Aug 21. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24027757 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of power spectral density of microvascular hemodynamics in skeletal muscles at very low and low-frequency via near-infrared diffuse optical spectroscopies.Biomed Opt Express. 2023 Oct 26;14(11):5994-6015. doi: 10.1364/BOE.502618. eCollection 2023 Nov 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2023. PMID: 38021143 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in tissue oxygen saturation measured by near-infrared spectroscopy in trauma patients after initial resuscitation are associated with occult shock.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2023 Feb;49(1):307-315. doi: 10.1007/s00068-022-02068-w. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2023. PMID: 36053289 Free PMC article.
-
An artificial intelligence system to predict the optimal timing for mechanical ventilation weaning for intensive care unit patients: A two-stage prediction approach.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 18;9:935366. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.935366. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36465940 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Machine-Learning Model for Prediction of Extubation Failure in Intensive Care Units.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 May 17;8:676343. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.676343. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34079812 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence of extubation failure and its predictors among adult patients in intensive care unit of low-resource setting: A prospective observational study.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 17;17(11):e0277915. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277915. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36395287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Esteban A, Alia I, Tobin M, Gil A, Gordo F, Vallverdu I, et al. Effect of spontaneous breathing trial duration on outcome of attempts to discontinue mechanical ventilation. Spanish Lung Failure Collaborative Group. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;159:512–518. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.159.2.9803106. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

