Safety of 80 antidepressants, antipsychotics, anti-attention-deficit/hyperactivity medications and mood stabilizers in children and adolescents with psychiatric disorders: a large scale systematic meta-review of 78 adverse effects
- PMID: 32394557
- PMCID: PMC7215080
- DOI: 10.1002/wps.20765
Safety of 80 antidepressants, antipsychotics, anti-attention-deficit/hyperactivity medications and mood stabilizers in children and adolescents with psychiatric disorders: a large scale systematic meta-review of 78 adverse effects
Abstract
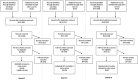
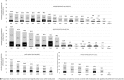
Mental disorders frequently begin in childhood or adolescence. Psychotropic medications have various indications for the treatment of mental dis-orders in this age group and are used not infrequently off-label. However, the adverse effects of these medications require special attention during developmentally sensitive periods of life. For this meta-review, we systematically searched network meta-analyses and meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials (RCTs), individual RCTs, and cohort studies reporting on 78 a priori selected adverse events across 19 categories of 80 psychotropic medications - including antidepressants, antipsychotics, anti-attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) medications and mood stabilizers - in children and adolescents with mental disorders. We included data from nine network meta-analyses, 39 meta-analyses, 90 individual RCTs, and eight cohort studies, including 337,686 children and adolescents. Data on ≥20% of the 78 adverse events were available for six antidepressants (sertraline, escitalopram, paroxetine, fluoxetine, venlafaxine and vilazodone), eight antipsychotics (risperidone, quetiapine, aripiprazole, lurasidone, paliperidone, ziprasidone, olanzapine and asenapine), three anti-ADHD medications (methylphenidate, atomoxetine and guanfacine), and two mood stabilizers (valproate and lithium). Among these medications with data on ≥20% of the 78 adverse events, a safer profile emerged for escitalopram and fluoxetine among antidepressants, lurasidone for antipsychotics, methylphenidate among anti-ADHD medications, and lithium among mood stabilizers. The available literature raised most concerns about the safety of venlafaxine, olanzapine, atomoxetine, guanfacine and valproate. Nausea/vomiting and discontinuation due to adverse event were most frequently associated with antidepressants; sedation, extrapyramidal side effects, and weight gain with antipsychotics; anorexia and insomnia with anti-ADHD medications; sedation and weight gain with mood stabilizers. The results of this comprehensive and updated quantitative systematic meta-review of top-tier evidence regarding the safety of antidepressants, antipsychotics, anti-ADHD medications and mood stabilizers in children and adolescents can inform clinical practice, research and treatment guidelines.
Keywords: Safety; adolescents; antidepressants; antipsychotics; children; meta-review; mood stabilizers; psychopharmacology; psychostimulants; tolerability.
© 2020 World Psychiatric Association.
Figures
References
-
- Parellada M. Why psychogeriatrics starts right after adolescence. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2013;22:391‐3. - PubMed
-
- Kessler RC, Berglund P, Demler O et al. Lifetime prevalence and age‐of‐onset distributions of DSM‐IV disorders in the national comorbidity survey replication. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2005;62:593‐602. - PubMed
-
- Chia MF, Cotton S, Filia K et al. Early intervention for bipolar disorder – Do current treatment guidelines provide recommendations for the early stages of the disorder? J Affect Disord 2019;257:669‐77. - PubMed
-
- Correll CU, Kratochvil CJ, March JS. Developments in pediatric psychopharmacology: focus on stimulants, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry 2011;72:655‐70. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

