Dietary Technologies to Optimize Healing from Injury-Induced Inflammation
- PMID: 32394845
- PMCID: PMC9906631
- DOI: 10.2174/1871523019666200512114210
Dietary Technologies to Optimize Healing from Injury-Induced Inflammation
Abstract
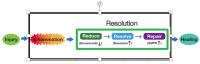
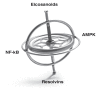
Inflammation is an acute adaptive response to injury. However, if the initial inflammatory response to an injury is not completely healed, it becomes chronic low-level inflammation that is strongly associated with many chronic disease states, including metabolic (obesity and diabetes), cardiovascular, auto-immune, and neurogenerative disorders as well as cancer. The healing process is far more complex than the initiation of inflammation. Within that complexity of healing is a sequence of events that are under profound dietary control and can be defined by specific blood markers. Those molecular events of the healing process that are under significant dietary control are termed as the Resolution Response. The purpose of this review is to describe the molecular components of the Resolution Response and how different dietary factors can either optimize or inhibit their actions. In particular, those dietary components that optimize the Resolution Response include a calorie-restricted, protein-adequate, moderate-carbohydrate, low-fat diet referred to as the Zone diet, omega-3 fatty acids, and polyphenols. The appropriate combination of these dietary interventions constitutes the foundation of Pro-Resolution Nutrition. The effect of these dietary components the actions of NF-κB, AMPK, eicosanoids, and resolvins are described in this review, as well as ranges of appropriate blood markers that indicate success in optimizing the Resolution Response by dietary interventions.
Keywords: AMPK; NF-κB; Resolution response; eicosanoids; inflammation; omega-3 fatty acids; polyphenols; resolvins; zone diet.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Figures
References
-
- Sears B. The Resolution Zone. Palm City, FL: Zone Press; 2019.
-
- Dubos R. Louis Pasteur: Freelance of Science. New York, NY: Little Brown; 1950.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

