Substandard and Falsified Antibiotics and Medicines against Noncommunicable Diseases in Western Cameroon and Northeastern Democratic Republic of Congo
- PMID: 32394884
- PMCID: PMC7410427
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.20-0184
Substandard and Falsified Antibiotics and Medicines against Noncommunicable Diseases in Western Cameroon and Northeastern Democratic Republic of Congo
Abstract
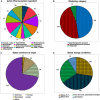
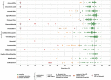
Falsified and substandard medicines may undermine the progress toward the Sustainable Development Goals. The present study investigated the quality of 13 essential medicines in Cameroon and the Democratic Republic of Congo (DR Congo). Five hundred six medicine samples were collected from the government and faith-based health facilities, private pharmacies, and informal vendors (total 60 facilities). Collected samples were analyzed according to the U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP) for identity, content, and dissolution of their active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and for uniformity of dosage units. Three samples (0.6%) were identified as falsified. Overall, 8.5% of the samples failed USP specifications for the content of the API and 11.7% failed dissolution testing. Medicines from informal vendors showed a higher out-of-specification rate (28.2%) than other types of drug outlets (12.3%; P < 0.0001). All three falsified medicines had been sold by informal vendors. The failure rate of medicines stated to be produced in Europe (5.1%) was lower than that for medicines from Asia (17.7%; P = 0.0049) and Africa (22.2%; P = 0.0042). Medicines against noncommunicable diseases showed a higher failure rate than antibiotics (25.3% versus 12.1%; P = 0.0004). Four hundred fifty-one of the samples were analyzed in Cameroon and the DR Congo with the Global Pharma Health Fund Minilab (thin-layer chromatography and disintegration testing). The three falsified medicines were readily detected in Minilab analysis. However, substandard samples were detected with low sensitivity. A well-enforced ban of medicine sales by informal vendors and increased attention to supplier qualification in the procurement process may reduce the prevalence of substandard and falsified medicines.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclaimer: The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Figures




References
-
- WHO , 2011. The World Medicines Situation 2011. Medicines Prices, Availability and Affordability. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; Available at: http://apps.who.int/medicinedocs/documents/s18065en/s18065en.pdf. Accessed February 14, 2020.
-
- Wilsdon T, Li I, 2016. The Evolution of Access to Essential Medicines for the Treatment of HIV/AIDS -Evidence From 2000 to 2015. Available at: https://www.ifpma.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/2016-The-Evolution-of-A.... Accessed February 14, 2020.
-
- UN-DESA , 2017. Sustainable Development Goal 3. Progress of Goal 3 in 2017. (E/2017/66). Available at: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/sdg3. Accessed February 14, 2020.
-
- Peyraud N, et al. 2017. An epidemic of dystonic reactions in central Africa. Lancet Glob Health 5: e137–e138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

