Interaction between delivery mode and maternal age in predicting overweight and obesity in 1,123 Chinese preschool children
- PMID: 32395518
- PMCID: PMC7210148
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2020.03.128
Interaction between delivery mode and maternal age in predicting overweight and obesity in 1,123 Chinese preschool children
Abstract
Background: Pediatric overweight/obesity has escalated to epidemic proportions worldwide. In this study, we aimed to assess the association of delivery mode and maternal age, both individually and interactively, with the risk of being overweight or obese among Chinese preschool children.
Methods: We cross-sectionally recruited 1,123 preschool children from five kindergartens in Beijing. Data were collected by a pre-validated self-developed questionnaire. Overweight and obesity are defined according to the World Health Organization (WHO), International Obesity Task Force (IOTF), and China criteria, respectively.
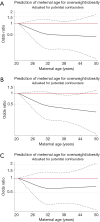
Results: Cesarean delivery was significantly associated with pediatric overweight/obesity under the WHO [adjusted odds ratio (aOR), 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.60, 1.12-2.29], IOTF (1.77, 1.23-2.53), and China (1.43, 1.06-1.94) criteria, respectively. Maternal age <28 years reached statistical significance under both WHO (1.69, 1.09-2.61) and IOTF (1.69, 1.09-2.61) criteria in predicting pediatric overweight/obesity. The interaction between cesarean delivery and maternal age <28 years was remarkably significant under the WHO (2.26, 1.10-4.67), IOTF (2.92, 1.43-5.96), and China (2.36, 1.24-4.50) criteria.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that the interaction between cesarean delivery and maternal age <28 years can remarkably increase the risk of overweight/obesity among Chinese preschool children.
Keywords: Delivery mode; maternal age; obesity; overweight; preschool children.
2020 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm.2020.03.128). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
