Serum levels of olfactomedin 4: a biomarker for asthma control state in asthmatics
- PMID: 32395538
- PMCID: PMC7210139
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2020.03.213
Serum levels of olfactomedin 4: a biomarker for asthma control state in asthmatics
Abstract
Background: Neutrophils are a key component of inflammation in asthma. Olfactomedin 4 (OLFM4) is produced by neutrophils and has been reported to be associated with asthma inflammation. We hypothesized that serum OLFM4 may be increased in asthmatic individuals and can assist with predicting asthma control state.
Methods: A total of 79 individuals were enrolled from Shenzhen People's Hospital, China and divided into 3 groups: uncontrolled asthmatics (n=35), controlled asthmatics (n=14), and healthy controls (n=30). The serum OLFM4 level was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clinical characteristics (such as age, gender, allergy history, body mass index (BIM), and smoking history), clinical indicators (such as whole blood count, sputum neutrophil, sputum eosinophil, forced expiratory volume in one second as percentage of predicted volume (FEV1% pred), IgE level, high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), and fractional expiratory nitric oxide (FeNO) were measured and the three groups were compared. The correlation between OLFM4 and the clinical characteristics and indicators was then evaluated. Finally, stepwise multiple regression analysis was performed to determine the contribution of clinical characteristics and clinical indicators influencing serum OLFM4 level.
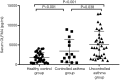
Results: Our results showed that the serum OLFM4 level was increased two-fold in the controlled asthma group (3,450.38±3,000.35 pg/mL) and three-fold in the uncontrolled asthma group (5,084.57±3,425.76 pg/mL), compared to the healthy control group (1,830.11±1,239.70 ng/mL) (P<0.001). We found a positive correlation between serum OLFM4 level and sputum neutrophils (P<0.001). OLFM4 was also found to be related to both hs-CRP level (P=0.007*) and blood neutrophil count (P<0.001). There were no significant associations identified between OLFM4 and age, gender, BMI, allergy, blood eosinophils, blood neutrophils, IgE, FeNO, or FEV1% pred.
Conclusions: Serum OLFM4 levels were increased in patients with asthma (the controlled asthma and uncontrolled asthma groups). There was a significant correlation between serum OLFM4 and levels of sputum neutrophil and hs-CRP, and OLFM4 was also related to both Hs-CRP level and blood neutrophil count. Serum OLFM4 level may serve as a useful biomarker for assessing asthma control state in asthmatic adults.
Keywords: Olfactomedin 4 (OLFM4); asthma; biomarkers.
2020 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm.2020.03.213). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Comment in
-
Olfactomedin 4 as a circulating biomarker for asthma.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Oct;10(20):1085. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3983. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36388787 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
