Age-related increase of kynurenine enhances miR29b-1-5p to decrease both CXCL12 signaling and the epigenetic enzyme Hdac3 in bone marrow stromal cells
- PMID: 32395570
- PMCID: PMC7210406
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bonr.2020.100270
Age-related increase of kynurenine enhances miR29b-1-5p to decrease both CXCL12 signaling and the epigenetic enzyme Hdac3 in bone marrow stromal cells
Abstract
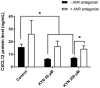
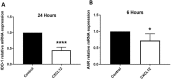
Mechanisms leading to age-related reductions in bone formation and subsequent osteoporosis are still incompletely understood. We recently demonstrated that kynurenine (KYN), a tryptophan metabolite, accumulates in serum of aged mice and induces bone loss. Here, we report on novel mechanisms underlying KYN's detrimental effect on bone aging. We show that KYN is increased with aging in murine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs). KYN reduces bone formation via modulating levels of CXCL12 and its receptors as well as histone deacetylase 3 (Hdac3). BMSCs responded to KYN by significantly decreasing mRNA expression levels of CXCL12 and its cognate receptors, CXCR4 and ACKR3, as well as downregulating osteogenic gene RUNX2 expression, resulting in a significant inhibition in BMSCs osteogenic differentiation. KYN's effects on these targets occur by increasing regulatory miRNAs that target osteogenesis, specifically miR29b-1-5p. Thus, KYN significantly upregulated the anti-osteogenic miRNA miR29b-1-5p in BMSCs, mimicking the up-regulation of miR-29b-1-5p in human and murine BMSCs with age. Direct inhibition of miR29b-1-5p by antagomirs rescued CXCL12 protein levels downregulated by KYN, while a miR29b-1-5p mimic further decreased CXCL12 levels. KYN also significantly downregulated mRNA levels of Hdac3, a target of miR-29b-1-5p, as well as its cofactor NCoR1. KYN is a ligand for the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). We hypothesized that AhR mediates KYN's effects in BMSCs. Indeed, AhR inhibitors (CH-223191 and 3',4'-dimethoxyflavone [DMF]) partially rescued secreted CXCL12 protein levels in BMSCs treated with KYN. Importantly, we found that treatment with CXCL12, or transfection with an miR29b-1-5p antagomir, downregulated the AhR mRNA level, while transfection with miR29b-1-5p mimic significantly upregulated its level. Further, CXCL12 treatment downregulated IDO, an enzyme responsible for generating KYN. Our findings reveal novel molecular pathways involved in KYN's age-associated effects in the bone microenvironment that may be useful translational targets for treating osteoporosis.
Keywords: AhR; CXCL12; Hdac3; Kynurenine; miR-29b-1-5p.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. William Hill, Sergio Mas Herrero, and Sudharsan Periyasamy-Thandavanis are inventors on U.S. Patent No. 9,267,139, “Compositions and Methods for Treating Musculoskeletal Disorders” issued. Ahmed Elmansi, Galina Kondrikova, Jessica Pierce, Helen Kaiser, Drs. Khaled Hussein, Xue Jiang, Alexandra Aguilar-Pérez, Dmitry Kondrikov, Nada H. Eisa, Ke-Hong Ding, Aisha Walker, Sadanand Fulzele, Wendy B. Bollag, Mohammed Elsalanty, Qing Zhong, Xing-ming Shi, Yun Su, Maribeth Johnson, Monte Hunter, Charles Reitman, Brian Volkman, Mark Hamrick, Carlos Isales, Meghan McGee-Lawrence have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Antebi B., Pelled G., Gazit D. Stem cell therapy for osteoporosis. Current osteoporosis reports. 2014;12(1):41–47. - PubMed
-
- Asai H., Hirata J., Watanabe-Akanuma M. Indoxyl glucuronide, a protein-bound uremic toxin, inhibits hypoxia-inducible factor–dependent erythropoietin expression through activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018;504(2):538–544. - PubMed
-
- Baglio S.R., Devescovi V., Granchi D., Baldini N. MicroRNA expression profiling of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells during osteogenic differentiation reveals Osterix regulation by miR-31. Gene. 2013;527(1):321–331. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

