Bmal1 integrates mitochondrial metabolism and macrophage activation
- PMID: 32396064
- PMCID: PMC7259948
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.54090
Bmal1 integrates mitochondrial metabolism and macrophage activation
Abstract
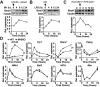
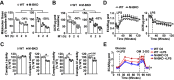
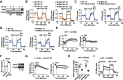
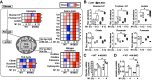
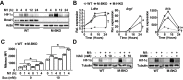
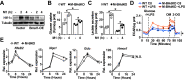
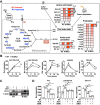
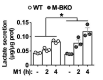
Metabolic pathways and inflammatory processes are under circadian regulation. Rhythmic immune cell recruitment is known to impact infection outcomes, but whether the circadian clock modulates immunometabolism remains unclear. We find that the molecular clock Bmal1 is induced by inflammatory stimulants, including Ifn-γ/lipopolysaccharide (M1) and tumor-conditioned medium, to maintain mitochondrial metabolism under metabolically stressed conditions in mouse macrophages. Upon M1 stimulation, myeloid-specific Bmal1 knockout (M-BKO) renders macrophages unable to sustain mitochondrial function, enhancing succinate dehydrogenase (SDH)-mediated mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species as well as Hif-1α-dependent metabolic reprogramming and inflammatory damage. In tumor-associated macrophages, aberrant Hif-1α activation and metabolic dysregulation by M-BKO contribute to an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Consequently, M-BKO increases melanoma tumor burden, whereas administering the SDH inhibitor dimethyl malonate suppresses tumor growth. Therefore, Bmal1 functions as a metabolic checkpoint that integrates macrophage mitochondrial metabolism, redox homeostasis and effector functions. This Bmal1-Hif-1α regulatory loop may provide therapeutic opportunities for inflammatory diseases and immunotherapy.
Keywords: anti-tumor activity; cell biology; energy metabolism; macrophage; mouse.
© 2020, Alexander et al.
Conflict of interest statement
RA, YL, NK, KS, CX, AH, SL, DJ, NL, CL No competing interests declared
Figures



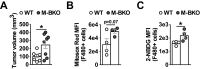
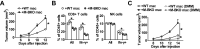

References
-
- Arts RJ, Plantinga TS, Tuit S, Ulas T, Heinhuis B, Tesselaar M, Sloot Y, Adema GJ, Joosten LA, Smit JW, Netea MG, Schultze JL, Netea-Maier RT. Transcriptional and metabolic reprogramming induce an inflammatory phenotype in non-medullary thyroid carcinoma-induced macrophages. OncoImmunology. 2016;5:e1229725. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1229725. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bell EL, Klimova TA, Eisenbart J, Moraes CT, Murphy MP, Budinger GR, Chandel NS. The qo site of the mitochondrial complex III is required for the transduction of hypoxic signaling via reactive oxygen species production. Journal of Cell Biology. 2007;177:1029–1036. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200609074. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Canaple L, Rambaud J, Dkhissi-Benyahya O, Rayet B, Tan NS, Michalik L, Delaunay F, Wahli W, Laudet V. Reciprocal regulation of brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha defines a novel positive feedback loop in the rodent liver circadian clock. Molecular Endocrinology. 2006;20:1715–1727. doi: 10.1210/me.2006-0052. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

