Quantum Dot-Catalyzed Photoreductive Removal of Sulfonyl-Based Protecting Groups
- PMID: 32396699
- PMCID: PMC7480491
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202005074
Quantum Dot-Catalyzed Photoreductive Removal of Sulfonyl-Based Protecting Groups
Abstract
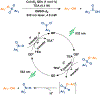
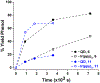
This Communication describes the use of CuInS2 /ZnS quantum dots (QDs) as photocatalysts for the reductive deprotection of aryl sulfonyl-protected phenols. For a series of aryl sulfonates with electron-withdrawing substituents, the rate of deprotection for the corresponding phenyl aryl sulfonates increases with decreasing electrochemical potential for the two electron transfers within the catalytic cycle. The rate of deprotection for a substrate that contains a carboxylic acid, a known QD-binding group, is accelerated by more than a factor of ten from that expected from the electrochemical potential for the transformation, a result that suggests that formation of metastable electron donor-acceptor complexes provides a significant kinetic advantage. This deprotection method does not perturb the common NHBoc or toluenesulfonyl protecting groups and, as demonstrated with an estrone substrate, does not perturb proximate ketones, which are generally vulnerable to many chemical reduction methods used for this class of reactions.
Keywords: copper indium sulfide; deprotection; phenylsulfonates; photocatalysis; quantum dots.
© 2020 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

References
-
- Mairanovsky VG, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 1976, 15, 281–292;
- Moussa Z, Romo D, Synlett 2006, 19, 3294–3298.
-
- Wuts PGM, Greene TW, Greene’s Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New Jersey, 2006, pp. 367–430.
-
- Maia HLS, Medeiros MJ, Montenegro MI, Court D, Pletcher D, J. Electroanal. Chem 1984, 164, 347–361.
-
- Falvey DE, Sundararajan C, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci 2004, 3, 831–838. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

