Respiratory disease in rhesus macaques inoculated with SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32396922
- PMCID: PMC7486227
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2324-7
Respiratory disease in rhesus macaques inoculated with SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
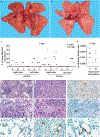
An outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), which is caused by a novel coronavirus (named SARS-CoV-2) and has a case fatality rate of approximately 2%, started in Wuhan (China) in December 20191,2. Following an unprecedented global spread3, the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a pandemic on 11 March 2020. Although data on COVID-19 in humans are emerging at a steady pace, some aspects of the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 can be studied in detail only in animal models, in which repeated sampling and tissue collection is possible. Here we show that SARS-CoV-2 causes a respiratory disease in rhesus macaques that lasts between 8 and 16 days. Pulmonary infiltrates, which are a hallmark of COVID-19 in humans, were visible in lung radiographs. We detected high viral loads in swabs from the nose and throat of all of the macaques, as well as in bronchoalveolar lavages; in one macaque, we observed prolonged rectal shedding. Together, the rhesus macaque recapitulates the moderate disease that has been observed in the majority of human cases of COVID-19. The establishment of the rhesus macaque as a model of COVID-19 will increase our understanding of the pathogenesis of this disease, and aid in the development and testing of medical countermeasures.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests
Figures
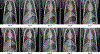
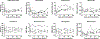

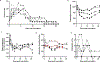
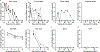
Update of
-
Respiratory disease and virus shedding in rhesus macaques inoculated with SARS-CoV-2.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Mar 21:2020.03.21.001628. doi: 10.1101/2020.03.21.001628. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Nature. 2020 Sep;585(7824):268-272. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2324-7. PMID: 32511299 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Organization, W. H. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports, <https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio...> (2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

