Investigating the Impact of Delivery System Design on the Efficacy of Self-Amplifying RNA Vaccines
- PMID: 32397231
- PMCID: PMC7348957
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines8020212
Investigating the Impact of Delivery System Design on the Efficacy of Self-Amplifying RNA Vaccines
Abstract
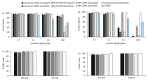
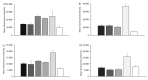
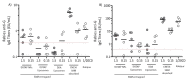
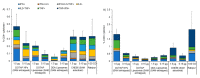
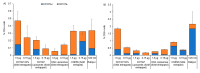
messenger RNA (mRNA)-based vaccines combine the positive attributes of both live-attenuated and subunit vaccines. In order for these to be applied for clinical use, they require to be formulated with delivery systems. However, there are limited in vivo studies which compare different delivery platforms. Therefore, we have compared four different cationic platforms: (1) liposomes, (2) solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs), (3) polymeric nanoparticles (NPs) and (4) emulsions, to deliver a self-amplifying mRNA (SAM) vaccine. All formulations contained either the non-ionizable cationic lipid 1,2-dioleoyl-3-trimethylammonium-propane (DOTAP) or dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide (DDA) and they were characterized in terms of physico-chemical attributes, in vitro transfection efficiency and in vivo vaccine potency. Our results showed that SAM encapsulating DOTAP polymeric nanoparticles, DOTAP liposomes and DDA liposomes induced the highest antigen expression in vitro and, from these, DOTAP polymeric nanoparticles were the most potent in triggering humoral and cellular immunity among candidates in vivo.
Keywords: antigen expression; emulsions; immunogenicity; liposomes; polymeric nanoparticles; self-amplifying RNA; solid lipid nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
G.A. and G.L. participated in the European Marie Curie PHA-ST-TRAIN-VAC PhD project at the University of Strathclyde (Glasgow, UK) in collaboration with GSK (Siena, Italy). The project was co-sponsored between the University of Strathclyde and GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA. Y.P. declare no conflict of interest. S.G, M.B., R.J., D.T.O. and B.C.B are employees of the GSK group of companies. All the authors declare that they have no other relevant affiliations or financial interests in conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Akinc A., Maier M.A., Manoharan M., Fitzgerald K., Jayaraman M., Barros S., Ansell S., Du X., Hope M.J., Madden T.D., et al. The Onpattro story and the clinical translation of nanomedicines containing nucleic acid-based drugs. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019;14:1084–1087. doi: 10.1038/s41565-019-0591-y. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

