iMethyl-Deep: N6 Methyladenosine Identification of Yeast Genome with Automatic Feature Extraction Technique by Using Deep Learning Algorithm
- PMID: 32397453
- PMCID: PMC7288457
- DOI: 10.3390/genes11050529
iMethyl-Deep: N6 Methyladenosine Identification of Yeast Genome with Automatic Feature Extraction Technique by Using Deep Learning Algorithm
Abstract
One of the most common and well studied post-transcription modifications in RNAs is N6-methyladenosine (m6A) which has been involved with a wide range of biological processes. Over the past decades, N6-methyladenosine produced some positive consequences through the high-throughput laboratory techniques but still, these lab processes are time consuming and costly. Diverse computational methods have been proposed to identify m6A sites accurately. In this paper, we proposed a computational model named iMethyl-deep to identify m6A Saccharomyces Cerevisiae on two benchmark datasets M6A2614 and M6A6540 by using single nucleotide resolution to convert RNA sequence into a high quality feature representation. The iMethyl-deep obtained 89.19% and 87.44% of accuracy on M6A2614 and M6A6540 respectively which show that our proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art predictors, at least 8.44%, 8.96%, 8.69% and 0.173 on M6A2614 and 15.47%, 28.52%, 25.54 and 0.5 on M6A6540 higher in terms of four metrics Sp, Sn, ACC and MCC respectively. Meanwhile, M6A6540 dataset never used to train a model.
Keywords: RNA N6-methyladenosine site; bioinformatics; computational biology; deep learning; methylation; yeast genome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
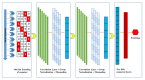
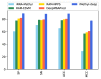
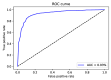

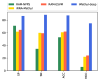


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

