Genome-Wide Association and Prediction of Traits Related to Salt Tolerance in Autotetraploid Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.)
- PMID: 32397526
- PMCID: PMC7247575
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21093361
Genome-Wide Association and Prediction of Traits Related to Salt Tolerance in Autotetraploid Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.)
Abstract
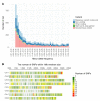
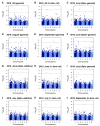
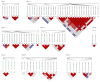
Soil salinity is a growing problem in world production agriculture. Continued improvement in crop salt tolerance will require the implementation of innovative breeding strategies such as marker-assisted selection (MAS) and genomic selection (GS). Genetic analyses for yield and vigor traits under salt stress in alfalfa breeding populations with three different phenotypic datasets was assessed. Genotype-by-sequencing (GBS) developed markers with allele dosage and phenotypic data were analyzed by genome-wide association studies (GWAS) and GS using different models. GWAS identified 27 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers associated with salt tolerance. Mapping SNPs markers against the Medicago truncatula reference genome revealed several putative candidate genes based on their roles in response to salt stress. Additionally, eight GS models were used to estimate breeding values of the training population under salt stress. Highest prediction accuracies and root mean square errors were used to determine the best prediction model. The machine learning methods (support vector machine and random forest) performance best with the prediction accuracy of 0.793 for yield. The marker loci and candidate genes identified, along with optimized GS prediction models, were shown to be useful in improvement of alfalfa with enhanced salt tolerance. DNA markers and the outcome of the GS will be made available to the alfalfa breeding community in efforts to accelerate genetic gains, in the development of biotic stress tolerant and more productive modern-day alfalfa cultivars.
Keywords: GBS; abiotic stress; allele dosage; association mapping; genomic selection; polyploid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Qadir M., Quillérou E., Nangia V., Murtaza G., Singh M., Thomas R., Drechsel P., Noble A. Economics of salt-induced land degradation and restoration. Nat. Resour. Forum. 2014;38:282–295. doi: 10.1111/1477-8947.12054. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

