Oral Chronic Toxicity of the Safe Tetrodotoxin Dose Proposed by the European Food Safety Authority and Its Additive Effect with Saxitoxin
- PMID: 32397553
- PMCID: PMC7291010
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins12050312
Oral Chronic Toxicity of the Safe Tetrodotoxin Dose Proposed by the European Food Safety Authority and Its Additive Effect with Saxitoxin
Abstract
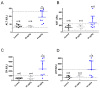
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a potent natural toxin causative of human food intoxications that shares its mechanism of action with the paralytic shellfish toxin saxitoxin (STX). Both toxins act as potent blockers of voltage-gated sodium channels. Although human intoxications by TTX were initially described in Japan, nowadays increasing concern about the regulation of this toxin in Europe has emerged due to its detection in fish and mollusks captured in European waters. Currently, TTX is only regularly monitored in Dutch fishery products. However, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has established a safety level of 44 µg/kg TTX as the amount of toxin that did not cause adverse effects in humans. This level was extrapolated considering initial data on its acute oral toxicity and EFSA remarked the need for chronic toxicity studies to further reduce the uncertainty of future toxin regulations. Thus, in this work, we evaluated the oral chronic toxicity of TTX using the safety levels initially recommended by EFSA in order to exclude potential human health risks associated with the worldwide expanding presence of TTX. Using internationally recommended guidelines for the assessment of oral chronic toxicity, the data provided here support the proposed safety level for TTX as low enough to prevent human adverse effects of TTX even after chronic daily exposure to the toxin. However, the combination of TTX with STX at doses above the maximal exposure level of 5.3 µg/kg body weight derived by EFSA increased the lethality of TTX, thus confirming that both TTX and paralytic shellfish toxins should be taken into account to assess human health risks.
Keywords: Tetrodotoxin; mollusk.; oral chronic toxicity; risk assessment; saxitoxin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Vlamis A., Katikou P., Rodriguez I., Rey V., Alfonso A., Papazachariou A., Zacharaki T., Botana A.M., Botana L.M. First detection of tetrodotoxin in greek shellfish by UPLC-MS/MS potentially linked to the presence of the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. Toxins. 2015;7:1779–1807. doi: 10.3390/toxins7051779. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2017 GRC GI-1682 (ED431C 2017/01)/Conselleria de Cultura, Educacion e Ordenación Universitaria, Xunta de Galicia,/International
- AGL2014-58210-R, AGL2016-78728-R (AEI/FEDER, UE), ISCIII/PI16/01830 and RTC-2016-5507-2, ITC-20161072/Centre for the Development of Industrial Technology (CDTI) and Technological Funds, supported by Ministerio de Economía, Industria y Competitividad/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

