Exploring Kinase Inhibition Properties of 9 H-pyrimido[5,4- b]- and [4,5- b]indol-4-amine Derivatives
- PMID: 32397570
- PMCID: PMC7281298
- DOI: 10.3390/ph13050089
Exploring Kinase Inhibition Properties of 9 H-pyrimido[5,4- b]- and [4,5- b]indol-4-amine Derivatives
Abstract
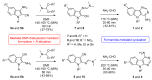
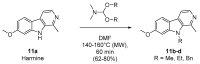
We previously highlighted the interest in 6,5,6-fused tricyclic analogues of 4-aminoquinazolines as kinase inhibitors in the micromolar to the nanomolar range of IC50 values. For the generation of chemical libraries, the formamide-mediated cyclization of the cyanoamidine precursors was carried out under microwave irradiation in an eco-friendly approach. In order to explore more in-depth the pharmacological interest in such tricyclic skeletons, the central five member ring, i.e., thiophène or furan, was replaced by a pyrrole to afford 9H-pyrimido[5,4-b]- and [4,5-b]indol-4-amine derivatives inspired from harmine. The inhibitory potency of the final products was determined against four protein kinases (CDK5/p25, CK1/ε, GSK3 and DYRK1A). As a result, we have identified promising compounds targeting CK1/ε and DYRK1A and displaying micromolar and submicromolar IC50 values.
Keywords: CDK5; CK1; DYRK1A; GSK-3; microwave-assisted chemistry; protein kinases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

