Oxidative Phosphorylation Dysfunction Modifies the Cell Secretome
- PMID: 32397676
- PMCID: PMC7246988
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21093374
Oxidative Phosphorylation Dysfunction Modifies the Cell Secretome
Abstract
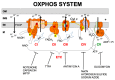
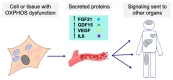
Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation disorders are extremely heterogeneous conditions. Their clinical and genetic variability makes the identification of reliable and specific biomarkers very challenging. Until now, only a few studies have focused on the effect of a defective oxidative phosphorylation functioning on the cell's secretome, although it could be a promising approach for the identification and pre-selection of potential circulating biomarkers for mitochondrial diseases. Here, we review the insights obtained from secretome studies with regard to oxidative phosphorylation dysfunction, and the biomarkers that appear, so far, to be promising to identify mitochondrial diseases. We propose two new biomarkers to be taken into account in future diagnostic trials.
Keywords: biomarkers; fibroblast growth factor 21; growth differentiation factor 15; interleukine-6; mitochondrial DNA; mitochondrial diseases; oxidative phosphorylation system; secretome; vascular endothelial growth factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lehr S., Hartwig S., Lamers D., Famulla S., Müller S., Hanisch F.G., Cuvelier C., Ruige J., Eckardt K., Ouwens D.M., et al. Identification and validation of novel adipokines released from primary human adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 2012;11:M111.010504. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.010504. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

