Development of remdesivir repositioning as a nucleotide analog against COVID-19 RNA dependent RNA polymerase
- PMID: 32397906
- PMCID: PMC7256352
- DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1767210
Development of remdesivir repositioning as a nucleotide analog against COVID-19 RNA dependent RNA polymerase
Abstract
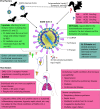
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the causative representative of a severe respiratory illness resulted in widespread human infections and deaths in nearly all of the countries since late 2019. There is no therapeutic FDA-approved drug against SARS-CoV-2 infection, although a combination of anti-viral drugs is directly being practiced in some countries. A broad-spectrum of antiviral agents are being currently evaluated in clinical trials, and in this review, we specifically focus on the application of Remdesivir (RVD) as a potential anti-viral compound against Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) -CoV, SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2. First, we overview the general information about SARS-CoV-2, followed by application of RDV as a nucleotide analogue which can potentially inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of COVs. Afterwards, we discussed the kinetics of SARS- or MERS-CoV proliferation in animal models which is significantly different compared to that in humans. Finally, some ongoing challenges and future perspective on the application of RDV either alone or in combination with other anti-viral agents against CoVs infection were surveyed to determine the efficiency of RDV in preclinical trials. As a result, this paper provides crucial evidence of the potency of RDV to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infections.Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
Keywords: COVID-19; Corona virus; MERS; SARS; SARS-CoV-2; anti-viral; remdesivir.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Remdesivir is a direct-acting antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency.J Biol Chem. 2020 May 15;295(20):6785-6797. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013679. Epub 2020 Apr 13. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32284326 Free PMC article.
-
The antiviral compound remdesivir potently inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus.J Biol Chem. 2020 Apr 10;295(15):4773-4779. doi: 10.1074/jbc.AC120.013056. Epub 2020 Feb 24. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32094225 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 polymerase by nucleotide analogs from a single-molecule perspective.Elife. 2021 Oct 7;10:e70968. doi: 10.7554/eLife.70968. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34617885 Free PMC article.
-
A review on the interaction of nucleoside analogues with SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Jun 30;181:605-611. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.112. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33766591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on Remdesivir: A Broad-spectrum Antiviral Molecule for Possible COVID-19 Treatment.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(17):2530-2543. doi: 10.2174/1389557521666210217093004. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33596800 Review.
Cited by
-
Quercetin inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection and prevents syncytium formation by cells co-expressing the viral spike protein and human ACE2.Virol J. 2024 Jan 25;21(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02299-w. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 38273400 Free PMC article.
-
Binding Mechanism of the Active Form of Molnupiravir to RdRp of SARS-CoV-2 and Designing Potential Analogues: Insights from Molecular Dynamics Simulations.ACS Omega. 2024 Sep 24;9(40):41583-41598. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c05469. eCollection 2024 Oct 8. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39398139 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 at a Glance: An Up-to-Date Overview on Variants, Drug Design and Therapies.Viruses. 2022 Mar 10;14(3):573. doi: 10.3390/v14030573. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35336980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nephrotoxicity of Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine in COVID-19 Patients.Adv Pharm Bull. 2021 Jan;11(1):6-7. doi: 10.34172/apb.2021.022. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Adv Pharm Bull. 2021. PMID: 33747847 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Exploring the interaction of quercetin-3-O-sophoroside with SARS-CoV-2 main proteins by theoretical studies: A probable prelude to control some variants of coronavirus including Delta.Arab J Chem. 2021 Oct;14(10):103353. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103353. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Arab J Chem. 2021. PMID: 34909059 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agostini M. L., Andres E. L., Sims A. C., Graham R. L., Sheahan T. P., Lu X., Smith E. C., Case J. B., Feng J. Y., Jordan R., Ray A. S., Cihlar T., Siegel D., Mackman R. L., Clarke M. O., Baric R. S., & Denison M. R. (2018). Coronavirus susceptibility to the antiviral remdesivir (GS-5734) is mediated by the viral polymerase and the proofreading exoribonuclease. MBio, 9(2), 218 10.1128/mBio.00221-18 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andersen P. I., Ianevski A., Lysvand H., Vitkauskiene A., Oksenych V., Bjørås M., Telling K., Lutsar I., Dumpis U., Irie Y., Tenson T., Kantele A., & Kainov D. E. (2020). Discovery and development of safe-in-man broad-spectrum antiviral agents. International Journal of Infectious Diseases: IJID: Official Publication of the International Society for Infectious Diseases, 93, 268–276. 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.02.018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
