The development of a questionnaire to assess leisure time screen-based media use and its proximal correlates in children (SCREENS-Q)
- PMID: 32397984
- PMCID: PMC7216486
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-020-08810-6
The development of a questionnaire to assess leisure time screen-based media use and its proximal correlates in children (SCREENS-Q)
Abstract
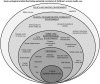
Background: The screen-media landscape has changed drastically during the last decade with wide-scale ownership and use of new portable touchscreen-based devices plausibly causing changes in the volume of screen media use and the way children and young people entertain themselves and communicate with friends and family members. This rapid development is not sufficiently mirrored in available tools for measuring children's screen media use. The aim of this study was to develop and evaluate a parent-reported standardized questionnaire to assess 6-10-year old children's multiple screen media use and habits, their screen media environment, and its plausible proximal correlates based on a suggested socio-ecological model.
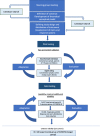
Methods: An iterative process was conducted developing the SCREENS questionnaire. Informed by the literature, media experts and end-users, a conceptual framework was made to guide the development of the questionnaire. Parents and media experts evaluated face and content validity. Pilot and field testing in the target group was conducted to assess test-retest reliability using Kappa statistics and intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC). Construct validity of relevant items was assessed using pairwise non-parametric correlations (Spearman's). The SCREENS questionnaire is based on a multidimensional and formative model.
Results: The SCREENS questionnaire covers six domains validated to be important factors of screen media use in children and comprises 19 questions and 92 items. Test-retest reliability (n = 37 parents) for continuous variables was moderate to substantial with ICC's ranging from 0.67 to 0.90. For relevant nominal and ordinal data, kappa values were all above 0.50 with more than 80% of the values above 0.61 indicating good test-retest reliability. Internal consistency between two different time use variables (from n = 243) showed good correlations with rho ranging from 0.59 to 0.66. Response-time was within 15 min for all participants.
Conclusions: SCREENS-Q is a comprehensive tool to assess children's screen media habits, the screen media environment and possible related correlates. It is a feasible questionnaire with multiple validated constructs and moderate to substantial test-retest reliability of all evaluated items. The SCREENS-Q is a promising tool to investigate children screen media use.
Keywords: Children; Correlates; Questionnaire; Screen-media use.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Danmarks Statistik . Elektronik i hjemmet. 2019.
-
- Asplund KM, Kair LR, Arain YH, Cervantes M, Oreskovic NM, Zuckerman KE. Early childhood screen time and parental attitudes toward child television viewing in a low-income Latino population attending the special supplemental nutrition program for women, infants, and children. Child Obes. 2015;11(5):590–599. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grontved A, Singhammer J, Froberg K, Moller NC, Pan A, Pfeiffer KA, et al. A prospective study of screen time in adolescence and depression symptoms in young adulthood. Prev Med. 2015;81:108–113. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical