Duodenal perforations secondary to a migrated biliary plastic stent successfully treated by endoscope: case-report and review of the literature
- PMID: 32398025
- PMCID: PMC7216602
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-020-01294-z
Duodenal perforations secondary to a migrated biliary plastic stent successfully treated by endoscope: case-report and review of the literature
Abstract
Background: Endoscopic retrograde biliary drainage (ERBD) is the most frequently performed procedure for treating benign or malignant biliary obstruction. Although duodenal perforations secondary to the biliary plastic stent are quite rare, they can be life-threatening. The treatment strategies for such perforations are diverse and continue to be debated.
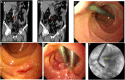
Case presentation: We report three cases of duodenal perforation due to the migration of biliary plastic stents that were successfully managed using an endoscope. The three patients were admitted on complaints of abdominal pain after they underwent ERBD. Abdominal computerized tomography (CT) revealed migration of the biliary plastic stents and perforation of the duodenum. Endoscopy was immediately performed, and perforation was confirmed. All migrated stents were successfully extracted endoscopically by using snares. In two of the three cases, the duodenal defects were successfully closed with haemostatic clips after stent retrieval, and subsequently, endoscopic nasobiliary drainage tubes were inserted. After the endoscopy and medical treatment, all three patients recovered completely.
Conclusions: Duodenal perforations due to the migration of biliary stents are rare, and the treatment strategies remain controversial. Our cases and cases in the literature demonstrate that abdominal CT is the preferred method of examination for such perforations, and endoscopic management is appropriate as a first-line treatment approach.
Keywords: Biliary stent; Case report; Duodenal perforation; Endoscope; Migration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Christensen M, Matzen P, Schulze S, et al. Complications of ERCP: a prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004;60(5):721–731. - PubMed
-
- Melita G, et al. Duodenal perforation secondary to biliary stent dislocation: a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Dermatol. 2005;4(1):92–97. - PubMed
-
- Aliperti G. Complications related to diagnostic and therapeutic endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Gastrointest Endosc Clin North Am. 1996;6:379–407. - PubMed
-
- Arhan M, et al. Migration of biliary plastic stents: experience of a tertiary center. Surg Endosc. 2009;23(4):769–775. - PubMed
-
- Johanson JF, Schmalz MJ, Geenen JE. Incidence and risk factors for biliary and pancreatic stent migration. Gastrointest Endosc. 1992;38(3):341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

