Morin inhibits Listeria monocytogenes virulence in vivo and in vitro by targeting listeriolysin O and inflammation
- PMID: 32398085
- PMCID: PMC7216731
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-020-01807-6
Morin inhibits Listeria monocytogenes virulence in vivo and in vitro by targeting listeriolysin O and inflammation
Abstract
Background: Listeria monocytogenes (L. monocytogenes) is a global opportunistic intracellular pathogen that can cause many infections, including meningitis and abortion in humans and animals; thus, L. monocytogenes poses a great threat to public safety and the development of the aquaculture industry. The isolation rate of Listeria monocytogenes in fishery products has always been high. And the pore-forming toxin listeriolysin O (LLO) is one of the most important virulence factors of L. monocytogenes. LLO can promote cytosolic bacterial proliferation and help the pathogen evade attacks from the host immune system. In addition, L. monocytogenes infection can trigger a series of severe inflammatory reactions.
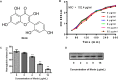
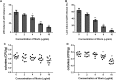
Results: Here, we further confirmed that morin lacking anti-Listeria activity could inhibit LLO oligomerization. We also found that morin can effectively alleviate the inflammation induced by Listeria in vivo and in vitro and exerted an obvious protective effect on infected cells and mice.
Conclusions: Morin does not possess anti-Listeria activity, neither does it interfere with secretion of LLO. However, morin inhibits oligomerisation of LLO and morin does reduce the inflammation caused during Listeria infection.
Keywords: Anti-infection; Inflammation; Listeria monocytogenes; Listeriolysin O,morin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
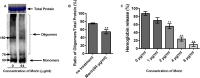
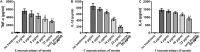
References
-
- Pensinger DA, Aliota MT, Schaenzer AJ, Boldon KM, Ansari IU, Vincent WJB, Knight B, Reniere ML, Striker R, Sauer JD. Selective pharmacologic inhibition of a PASTA kinase increases Listeria monocytogenes susceptibility to beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(8):4486–4494. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jordan K, McAuliffe O. Listeria monocytogenes in foods. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2018;86:181–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

