Impact of PD-1 Blockade on Severity of COVID-19 in Patients with Lung Cancers
- PMID: 32398243
- PMCID: PMC7416461
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0596
Impact of PD-1 Blockade on Severity of COVID-19 in Patients with Lung Cancers
Erratum in
-
Correction: Impact of PD-1 Blockade on Severity of COVID-19 in Patients with Lung Cancers.Cancer Discov. 2021 Feb;11(2):520. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1818. Cancer Discov. 2021. PMID: 33531427 No abstract available.
Abstract
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has led to dramatic changes in oncology practice. It is currently unknown whether programmed death 1 (PD-1) blockade therapy affects severity of illness from COVID-19 in patients with cancer. To address this uncertainty, we examined consecutive patients with lung cancers who were diagnosed with COVID-19 and examined severity on the basis of no or prior receipt of PD-1 blockade. Overall, the severity of COVID-19 in patients with lung cancer was high, including need for hospitalization in more than half of patients and death in nearly a quarter. Prior PD-1 blockade was, as expected, associated with smoking status. After adjustment for smoking status, PD-1 blockade exposure was not associated with increased risk of severity of COVID-19. PD-1 blockade does not appear to affect the severity of COVID-19 in patients with lung cancers. SIGNIFICANCE: A key question in oncology practice amidst the COVID-19 pandemic is whether PD-1 blockade therapy affects COVID-19 severity. Our analysis of patients with lung cancers supports the safety of PD-1 blockade treatment to achieve optimal cancer outcomes.This article is highlighted in the In This Issue feature, p. 1079.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
I.R. Preeshagul has served on an advisory board for Pfizer and AstraZeneca. J.D. Wolchok is a consultant at Astellas, Kyowa Hakko Kirin, Truvax, Sellas, Serametrix, Surface Oncology, Syndax, Syntalogic, Amgen, Ascentage, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck, Neon Therapeutics, Polynoma, Psioxus, Recepta, Takara, Trieza, and Elucida; reports receiving commercial research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca, and Sephora; and has ownership interest (including patents) in Tizona Therapeutics, Adaptive Biotech, anti-CTLA4 antibodies, anti-GITR antibodies and methods of use thereof, Imvaq, Beigene, Linneaus, Arsenal IO, Apricity, myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC) assay, xenogeneic DNA vaccines, and anti-PD1 antibody. M.D. Hellmann is a consultant at Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Achilles, Arcus, AstraZeneca, Genentech/Roche, Nektar, Syndax, Mirati, Shattuck Labs, Immunai, and Blueprint Medicines; reports receiving a commercial research grant from Bristol-Myers Squibb; has ownership interest (including patents) in Shattuck Labs, Immunai, Arcus, and PCT/US2015/062208, and has received travel support/honoraria from AstraZeneca, Eli Lilly, and Bristol-Myers Squibb. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures

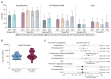
References
-
- Lewis MA. Between scylla and charybdis - oncologic decision making in the time of COVID-19. N Engl J Med 2020 Apr 7. [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
-
- Lewnard JA, Liu VXJ ML, Schmidt MA. Incidence, clinical outcomes, and transmission dynamics of hospitalized 2019 coronavirus disease among 9,596,321 individuals residing in California and Washington, United States: a prospective cohort study. MedRxiv 2020.
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention. JAMA 2020 Feb 24. [Epub ahead of print]. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

