Risk factors for viral RNA shedding in COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 32398298
- PMCID: PMC7236829
- DOI: 10.1183/13993003.01190-2020
Risk factors for viral RNA shedding in COVID-19 patients
Abstract
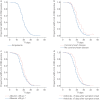
The median time of SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA shedding was 19 days. Patients with coronary heart disease comorbidity or decreased albumin levels experienced delays in clearance of SARS-CoV-2 RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Y. Fu has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: P. Han has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: R. Zhu has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: T. Bai has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: J. Yi has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: X. Zhao has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Tao has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: R. Quan has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: C. Chen has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: Y. Zhang has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: Q. He has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Jing has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: X. Xiong has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: D. Tian has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: W. Yan has nothing to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak situation. www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 Date last accessed: 25 April 2020.
-
- World Health Organization WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 – 11 March 2020. www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at... Date last updated: 11 March 2020. Date last accessed: 25 April 2020.
-
- National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia (Trial Version 7) www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-03/04/content_5486705.htm Date last updated: 3 March 2020. Date last accessed: 25 April 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
