Description of Covid-19 Cases in Brazil and Italy
- PMID: 32399516
- PMCID: PMC7216125
- DOI: 10.1007/s42399-020-00307-y
Description of Covid-19 Cases in Brazil and Italy
Abstract
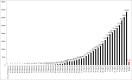
The emergence of Covid-19 started in China and has rapidly spread across the globe, notably in Italy and more recently to Brazil. This is a very worrying situation for the affected countries. This Brief Communication aims to describe and correlate the number of confirmed cases and deaths of Covid-19 in Brazil and Italy. This is a descriptive and retrospective study that used data collated on the World Health Organization (WHO) online platform between 21 January and 19 April 2020. After analyzing the data, it was observed that the number of confirmed cases and deaths in Brazil is lower than that in Italy. There are certain factors in Brazil which see it in a lower risk position than Italy; however, despite the current slow spread of the virus, the situation in Brazil is difficult to predict.
Keywords: 2019-nCoV; COVID-19; Coronavirus disease; Epidemiology; Pandemic.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. WHO travel advice for international travel and trade in relation to the outbreak of pneumonia caused by a new coronavirus in China. 2020; Available from: https://www.who.int/ith/20200901_outbreak_of_Pneumonia_caused_by_a_new_c... Accessed 20 March 2020.
-
- Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, Niu P, Zhan F, Ma X, Wang D, Xu W, Wu G, Gao GF, Tan W, China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(8):727–733. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO. Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV): situation report – 90. 2020; Available from: https://wwwwhoint/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/202... Acessed 18 April 2020.
-
- WHO. Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV): situation report – 11. 2020; Available from: https://wwwwhoint/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/202... Acessed 20 March 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous