Differential expression of microRNA in serum fractions and association of Argonaute 1 microRNAs with heart failure
- PMID: 32400052
- PMCID: PMC7299714
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15306
Differential expression of microRNA in serum fractions and association of Argonaute 1 microRNAs with heart failure
Abstract
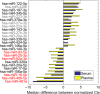
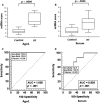
The serum or plasma microRNA (miRNA) molecules have been suggested as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, in various pathological conditions. However, these molecules are also found in different serum fractions, such as exosomes and Argonaute (Ago) protein complexes. Ago1 is the predominant Ago protein expressed in heart tissue. The objective of the study was to examine the hypothesis that Ago1-associated miRNAs may be more relevant to cardiac disease and heart failure compared with the serum. In total, 84 miRNA molecules were screened for their expression in the whole serum, exosomes and Ago1, and Ago2 complexes. Ago1-bound miR-222-3p, miR-497-5p and miR-21-5p were significantly higher, and let-7a-5p was significantly lower in HF patients compared with healthy controls, whereas no such difference was observed for those markers in the serum samples among the groups. A combination of these 4 miRNAs into an Ago1-HF score provided a ROC curve with an AUC of 1, demonstrating clear discrimination between heart failure patients and healthy individuals. Ago1 fraction might be a better and more specific platform for identifying HF-related miRNAs compared with the whole serum.
Keywords: argonaute; heart failure; microRNA.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by Rosetta Genomics Ltd, Rehovot, Israel. The following authors are employed by Rosetta: Eti Meiri, Nir Dromi, Sharon Kredo‐Russo, Hila Benjamin, Sarit Tabak, Hagai Marmor, Maria Motin, Danit Lebanony, Gila Lithwick‐Yanai, and Etti Kadosh.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

