Toll-like Receptor 4 Deficiency Aggravates Airway Hyperresponsiveness and Inflammation by Impairing Neutrophil Apoptosis in a Toluene Diisocyanate-Induced Murine Asthma Model
- PMID: 32400128
- PMCID: PMC7225000
- DOI: 10.4168/aair.2020.12.4.608
Toll-like Receptor 4 Deficiency Aggravates Airway Hyperresponsiveness and Inflammation by Impairing Neutrophil Apoptosis in a Toluene Diisocyanate-Induced Murine Asthma Model
Abstract
Purpose: Accumulating evidence has suggested that toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is critically involved in the pathogenesis of asthma. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of TLR4 in toluene diisocyanate (TDI)-induced allergic airway inflammation.
Methods: TLR4-/- and wild-type (WT) C57BL/10J mice were sensitized and challenged with TDI to generate a TDI-induced asthma model. B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) inhibitors, ABT-199 (4 mg/kg) and ABT-737 (4 mg/kg), were intranasally given to TDI-exposed TLR4-/- mice after each challenge.
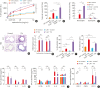
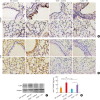
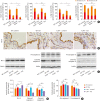
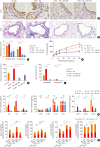
Results: TDI exposure led to increased airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR), granulocyte flux, bronchial epithelial shedding and extensive submucosal collagen deposition, which were unexpectedly aggravated by TLR4 deficiency. Following TDI challenge, TLR4-/- mice exhibited down-regulated interleukin-17A and increased colony-stimulating factor 3 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), while WT mice did not. In addition, TLR4 deficiency robustly suppressed the expression of NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 and NLR family CARD domain containing 4, decreased caspase-1 activity in TDI-exposed mice, but had no effect on the level of high mobility group box 1 in BALF. Flow cytometry revealed that TDI hampered both neutrophil and eosinophil apoptosis, of which neutrophil apoptosis was further inhibited in TDI-exposed TLR4-/- mice, with marked up-regulation of Bcl-2. Moreover, inhibition of Bcl-2 with either ABT-199 or ABT-737 significantly alleviated neutrophil recruitment by promoting apoptosis.
Conclusions: These data indicated that TLR4 deficiency promoted neutrophil infiltration by impairing its apoptosis via up-regulation of Bcl-2, thereby resulting in deteriorated AHR and airway inflammation, which suggests that TLR4 could be a negative regulator of TDI-induced neutrophilic inflammation.
Keywords: Toll-like receptor 4; apoptosis; asthma; neutrophlic inflammation; toluene diisocyanate.
Copyright © 2020 The Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology · The Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no financial or other issues that might lead to conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Masoli M, Fabian D, Holt S, Beasley R Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) Program. The global burden of asthma: executive summary of the GINA Dissemination Committee report. Allergy. 2004;59:469–478. - PubMed
-
- Kim RY, Pinkerton JW, Essilfie AT, Robertson AA, Baines KJ, Brown AC, et al. Role for NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated, IL-1β-dependent responses in severe, steroid-resistant asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;196:283–297. - PubMed
-
- Tang H, Li T, Han X, Sun J. TLR4 antagonist ameliorates combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome (CARAS) by reducing inflammatory monocytes infiltration in mice model. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;73:254–260. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 2017YFC1310601/National Key R&D Program of China/China
- 81871266/NSFC/National Natural Science Foundation of China/China
- 81800022/NSFC/National Natural Science Foundation of China/China
- 201604020012/Guangzhou Healthcare Collaborative Innovation Major Project/China
- 201604020008/Scientific and Technological Project of Guangzhou/China

