In vivo measurement of widespread synaptic loss in Alzheimer's disease with SV2A PET
- PMID: 32400950
- PMCID: PMC7383876
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.12097
In vivo measurement of widespread synaptic loss in Alzheimer's disease with SV2A PET
Abstract
Introduction: Synaptic loss is a robust and consistent pathology in Alzheimer's disease (AD) and the major structural correlate of cognitive impairment. Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging of synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2A (SV2A) has emerged as a promising biomarker of synaptic density.
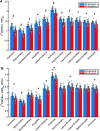
Methods: We measured SV2A binding in 34 participants with early AD and 19 cognitively normal (CN) participants using [11 C]UCB-J PET and a cerebellar reference region for calculation of the distribution volume ratio.
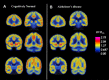
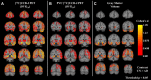
Results: We observed widespread reductions of SV2A binding in medial temporal and neocortical brain regions in early AD compared to CN participants. These reductions were largely maintained after correction for volume loss and were more extensive than decreases in gray matter volume.
Conclusion: We were able to measure widespread synaptic loss due to AD using [11 C]UCB-J PET. Future studies will continue to evaluate the utility of SV2A PET for tracking AD progression and for monitoring potential therapies.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; SV2A; [11C]UCB-J | PET; synaptic density.
© 2020 The Authors. Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Figures
Comment in
-
Synaptic impairment: The new battlefield of Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2021 Feb;17(2):314-315. doi: 10.1002/alz.12189. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Alzheimers Dement. 2021. PMID: 32946657 No abstract available.
-
Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association.Alzheimers Dement. 2021 Feb;17(2):316-317. doi: 10.1002/alz.12190. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Alzheimers Dement. 2021. PMID: 33047474 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Scheff SW, DeKosky ST, Price DA. Quantitative assessment of cortical synaptic density in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1990;11:29‐37. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ. Alzheimer's disease is a synaptic failure. Science. 2002;298:789‐791. - PubMed
-
- Terry RD, Masliah E, Salmon DP, et al. Physical basis of cognitive alterations in Alzheimer's disease: synapse loss is the major correlate of cognitive impairment. Ann Neurol. 1991;30:572‐580. - PubMed
-
- DeKosky ST, Scheff SW. Synapse loss in frontal cortex biopsies in Alzheimer's disease: correlation with cognitive severity. Ann Neurol. 1990;27:457‐464. - PubMed
-
- DeKosky ST, Scheff SW, Styren SD. Structural correlates of cognition in dementia: quantification and assessment of synapse change. Neurodegeneration. 1996;5:417‐421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RF1AG057553/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23 AG057794/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057553/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG052560/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50AG047270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K23AG057784/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG052560/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG062276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066508/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG062276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH019961/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG047270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG057784/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000142/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

