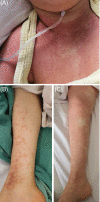
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis after COVID-19 treatment with hydroxychloroquine
- PMID: 32401410
- PMCID: PMC7261985
- DOI: 10.1111/dth.13565
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis after COVID-19 treatment with hydroxychloroquine
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment on
-
Hydroxychloroquine and ivermectin: A synergistic combination for COVID-19 chemoprophylaxis and treatment?J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jun;82(6):e221. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.017. Epub 2020 Apr 10. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 32283237 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) Situation Report—100. https://www.who.int/docs/default‐source/coronaviruse/situation‐reports/2.... Accessed April 30, 2020.
-
- Observatoire National des Maladies Nouvelles et Émergentes . Note sur la situation épidémiologique du ‘COVID‐19’ à la date du 26 Avril 2020. http://www.onmne.tn/fr/images/COVID-19-dernier-bulletin.pdf. Accessed April 30, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources