Epidemiology and outcome of high-surgical-risk patients admitted to an intensive care unit in Brazil
- PMID: 32401988
- PMCID: PMC7206944
- DOI: 10.5935/0103-507x.20200005
Epidemiology and outcome of high-surgical-risk patients admitted to an intensive care unit in Brazil
Abstract
Objective: To define the epidemiological profile and the main determinants of morbidity and mortality in noncardiac high surgical risk patients in Brazil.
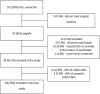
Methods: This was a prospective, observational and multicenter study. All noncardiac surgical patients admitted to intensive care units, i.e., those considered high risk, within a 1-month period were evaluated and monitored daily for a maximum of 7 days in the intensive care unit to determine complications. The 28-day postoperative, intensive care unit and hospital mortality rates were evaluated.
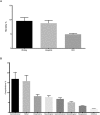
Results: Twenty-nine intensive care units participated in the study. Surgeries were performed in 25,500 patients, of whom 904 (3.5%) were high-risk (95% confidence interval - 95%CI 3.3% - 3.8%) and were included in the study. Of the participating patients, 48.3% were from private intensive care units, and 51.7% were from public intensive care units. The length of stay in the intensive care unit was 2.0 (1.0 - 4.0) days, and the length of hospital stay was 9.5 (5.4 - 18.6) days. The complication rate was 29.9% (95%CI 26.4 - 33.7), and the 28-day postoperative mortality rate was 9.6% (95%CI 7.4 - 12.1). The independent risk factors for complications were the Simplified Acute Physiology Score 3 (SAPS 3; odds ratio - OR = 1.02; 95%CI 1.01 - 1.03) and Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score (SOFA) on admission to the intensive care unit (OR = 1.17; 95%CI 1.09 - 1.25), surgical time (OR = 1.001, 95%CI 1.000 - 1.002) and emergency surgeries (OR = 1.93, 95%CI, 1.10 - 3.38). In addition, there were associations with 28-day mortality (OR = 1.032; 95%CI 1.011 - 1.052), SAPS 3 (OR = 1.041; 95%CI 1.107 - 1.279), SOFA (OR = 1.175, 95%CI 1.069 - 1.292) and emergency surgeries (OR = 2.509; 95%CI 1.040 - 6.051).
Conclusion: Higher prognostic scores, elderly patients, longer surgical times and emergency surgeries were strongly associated with higher 28-day mortality and more complications during the intensive care unit stay.
Objetivo: Definir o perfil epidemiológico e os principais determinantes de morbimortalidade dos pacientes cirúrgicos não cardíacos de alto risco no Brasil.
Métodos: Estudo prospectivo, observacional e multicêntrico. Todos os pacientes cirúrgicos não cardíacos admitidos nas unidades de terapia intensiva, ou seja, considerados de alto risco, no período de 1 mês, foram avaliados e acompanhados diariamente por, no máximo, 7 dias na unidade de terapia intensiva, para determinação de complicações. As taxas de mortalidade em 28 dias de pós-operatório, na unidade de terapia intensiva e hospitalar foram avaliadas.
Resultados: Participaram 29 unidades de terapia intensiva onde foram realizadas cirurgias em 25.500 pacientes, dos quais 904 (3,5%) de alto risco (intervalo de confiança de 95% - IC95% 3,3% - 3,8%), tendo sido incluídos no estudo. Dos pacientes envolvidos, 48,3% eram de unidades de terapia intensiva privadas e 51,7% de públicas. O tempo de internação na unidade de terapia intensiva foi de 2,0 (1,0 - 4,0) dias e hospitalar de 9,5 (5,4 - 18,6) dias. As taxas de complicações foram 29,9% (IC95% 26,4 - 33,7) e mortalidade em 28 dias pós-cirurgia 9,6% (IC95% 7,4 - 12,1). Os fatores independentes de risco para complicações foram Simplified Acute Physiology Score 3 (SAPS 3; razão de chance − RC = 1,02; IC95% 1,01 - 1,03) e Sequential Organ Failure Assessment Score (SOFA) da admissão na unidade de terapia intensiva (RC =1,17; IC95% 1,09 - 1,25), tempo de cirurgia (RC = 1,001; IC95% 1,000 - 1,002) e cirurgias de emergências (RC = 1,93; IC95% 1,10 - 3,38). Em adição, foram associados com mortalidade em 28 dias idade (RC = 1,032; IC95% 1,011 - 1,052) SAPS 3 (RC = 1,041; IC95% 1,107 - 1,279), SOFA (RC = 1,175; IC95% 1,069 - 1,292) e cirurgias emergenciais (RC = 2,509; IC95% 1,040 - 6,051).
Conclusão: Pacientes com escores prognósticos mais elevados, idosos, tempo cirúrgico e cirurgias emergenciais estiveram fortemente associados a maior mortalidade em 28 dias e mais complicações durante permanência em unidade de terapia intensiva.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Ghaferi AA, Birkmeyer JD, Dimick JB. Variation in hospital mortality associated with inpatient surgery. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(14):1368–1375. - PubMed
-
- Jhanji S, Thomas B, Ely A, Watson D, Hinds CJ, Pearse RM. Mortality and utilisation of critical care resources amongst high-risk surgical patients in a large NHS trust. Anaesthesia. 2008;63(7):695–700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

