The role of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in isolated intrathoracic lymphadenopathy in non-neoplastic patients: a common dilemma in clinical practice
- PMID: 32402011
- PMCID: PMC7462701
- DOI: 10.36416/1806-3756/e20180183
The role of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in isolated intrathoracic lymphadenopathy in non-neoplastic patients: a common dilemma in clinical practice
Abstract
Objective: To determine the diagnostic yield of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) in non-neoplastic patients with isolated intrathoracic lymphadenopathy (IL).
Methods: This was a retrospective study of patients with isolated IL referred for EBUS-TBNA. We calculated the sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) of EBUS-TBNA in the diagnosis of granulomatous, reactive, and neoplastic lymphadenopathy. In cases of nonspecific granulomas, reactive lymphadenopathy, or inconclusive results, a definitive diagnosis was established by other diagnostic procedures or during a follow-up period of at least 18 months.
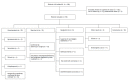
Results: Among the 58 patients included in the study, EBUS-TBNA established a diagnosis of granulomatous disease in 22 (38%), reactive lymphadenopathy in 15 (26%), cancer in 8 (14%), and other diseases in 3 (5%). Results were inconclusive in 10 (17%), the diagnosis being established by other bronchoscopic procedures in 2 (20%) and by surgical procedures in 8 (80%). A final diagnosis of reactive lymphadenopathy was established in 12. Of those, 11 (92%) had their diagnosis confirmed during follow-up and 1 (8%) had their diagnosis confirmed by mediastinoscopy. In another 3, a final diagnosis of sarcoidosis or neoplasm was established. For the diagnosis of granulomatous disease, neoplasms, and reactive lymphadenopathy, EBUS-TBNA was found to have a sensitivity of 73%, 68%, and 92%, respectively; a specificity of 100%, 100%, and 93%, respectively; an accuracy of 86%, 93%, and 93%, respectively; a PPV of 100%, 100%, and 80%, respectively; and an NPV of 78%, 92%, and 98%, respectively.
Conclusions: In non-neoplastic patients, granulomatous disease and reactive lymphadenopathy appear to be common causes of isolated IL. EBUS-TBNA shows promising results as a first-line minimally invasive diagnostic procedure. The results obtained by EBUS-TBNA can be optimized by examining clinical and radiological findings during follow-up or by comparison with the results obtained with other bronchoscopic methods.
Objetivo:: Determinar o rendimento diagnóstico da endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA, aspiração transbrônquica com agulha guiada por ultrassonografia endobrônquica) em pacientes não neoplásicos com linfonodomegalia intratorácica (LI) isolada.
Métodos:: Estudo retrospectivo com pacientes com LI isolada encaminhados para EBUS-TBNA. Foram calculados a sensibilidade, especificidade, precisão, valor preditivo positivo (VPP) e valor preditivo negativo (VPN) da EBUS-TBNA no diagnóstico de linfadenopatia granulomatosa, reacional e neoplásica. Em casos de granulomas inespecíficos, linfadenopatia reacional ou resultados inconclusivos, o diagnóstico definitivo foi estabelecido por meio de outros procedimentos diagnósticos ou ao longo de pelo menos 18 meses de acompanhamento.
Resultados:: Nos 58 pacientes incluídos, a EBUS-TBNA permitiu que se estabelecesse o diagnóstico de doença granulomatosa em 22 (38%), linfadenopatia reacional em 15 (26%), câncer em 8 (14%) e outras doenças em 3 (5%). Os resultados foram inconclusivos em 10 (17%), nos quais o diagnóstico foi feito por meio de outros procedimentos broncoscópicos, em 2 (20%), ou de procedimentos cirúrgicos, em 8 (80%). O diagnóstico final de linfadenopatia reacional foi feito em 12. Destes, 11 (92%) receberam confirmação diagnóstica durante o acompanhamento e 1 (8%), por meio de mediastinoscopia. Em outros 3, o diagnóstico final foi sarcoidose ou neoplasia. Para o diagnóstico de doença granulomatosa, câncer e linfadenopatia reacional, a EBUS-TBNA apresentou sensibilidade de 73%, 68% e 92%, respectivamente; especificidade de 100%, 100% e 93%, respectivamente; precisão de 86%, 93% e 93%, respectivamente; VPP de 100%, 100% e 80%, respectivamente; VPN de 78%, 92% e 98%, respectivamente.
Conclusões:: Em pacientes não neoplásicos, doenças granulomatosas e linfadenopatia reacional parecem ser causas comuns de LI isolada. A EBUS-TBNA apresenta resultados promissores como procedimento diagnóstico minimamente invasivo de primeira linha. Os resultados obtidos pela EBUS-TBNA podem ser otimizados pelos achados clínicos e radiológicos durante o acompanhamento ou pela comparação com os resultados de outros métodos broncoscópicos.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

