Evaluation of two automated and three rapid lateral flow immunoassays for the detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies
- PMID: 32403010
- PMCID: PMC7198434
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104413
Evaluation of two automated and three rapid lateral flow immunoassays for the detection of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies
Abstract
Introduction: Several SARS-CoV-2 immunoassays have been developed recently. The purpose of this study was to assess the performance of five immunoassays for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies.
Methods: Two quantitative automated immunoassays (Maglumi™2019-n-Cov IgG and IgM and Euroimmun Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG and IgA assays) and three lateral flow rapid tests were performed. This retrospective study included 200 residual sera from patients and healthy volunteers. Case serum samples (n = 128) were obtained from COVID-19 patients confirmed by RT-qPCR and CT-scan. Days since onset of symptoms was collected from their medical records. Control non-SARS-CoV-2 samples (n = 72) were obtained from anonymous stored residual serum samples.
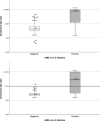
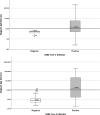
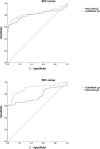
Results: Maglumi™ IgG/IgM tests showed overall less sensitivity than Euroimmun IgG/IgA test (84.4 % versus 64.3 %). Both tests showed similar specificities of IgG at 99 % and 100 %, respectively. The results from the lateral flow assays were easily interpretable with unambiguous coloured reading bands. The overall sensitivity of the three tests was similar (around 70 %) without any significant differences. The sensitivity of the three lateral flow assays and also of the serological quantitative assays increased during the second week after symptom onset and all reached similar values (91 %-94 %) after 14 days.
Conclusion: This study shows accurate and equivalent performance of the five serological antibody assays (ELISA, CLIA and three lateral flow tests) in detecting SARS-CoV-2 antibodies 14 days after the onset of COVID-19 symptoms. This is compatible with their application in specific clinical contexts and in determining epidemiological strategies for the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: CLIA; COVID-19; ELISA; Immunoassays; Lateral flow assays; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . 2020. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-2019) Situation Reports.https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019
-
- World Health Organization . 2020. COVID 19 Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC): Global Research and Innovation Forum: Towards a Research Roadmap. Geneva: 11–12 February.
-
- SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic pipeline n.d. https://www.finddx.org/covid-19/pipeline/. (Accessed April 23, 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

