The Anxiety Status of Chinese Medical Workers During the Epidemic of COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 32403209
- PMCID: PMC7265026
- DOI: 10.30773/pi.2020.0127
The Anxiety Status of Chinese Medical Workers During the Epidemic of COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objective: To analysis the anxiety status of Chinese medical workers during the epidemic of COVID-19 by meta-analysis method.
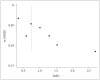
Methods: CNKI, VIP, WanFang Data, SinoMed, PubMed, Cochrane, EMBASE, MEDLINE, Scopus, Google Scholar and other databases were searched to collect literature on the anxiety status of Chinese medical workers during the epidemic of COVID-19. The retrieval time is from the database construction to 11/03/2020. Meta-analysis was performed on the included articles by using Stata 16.0 software.
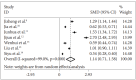
Results: A total of 7 articles were included, with a total sample size of 7,741 people. Meta-analysis using the random effects model showed that the anxiety score of Chinese medical during the epidemic of COVID-19 was significantly higher than that of the national norm in each study, the difference was statistically significant [SMD (95% CI)=1.145 (0.705-1.584), p<0.001].
Conclusion: The anxiety level of Chinese medical workers has increased significantly during the epidemic of COVID-19.
Keywords: Anxiety; COVID-19; China; Medical staff; Meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Available at: http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2020-01/21/content_5471164.htm. Accessed March 12, 2020. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang L, Yanrui J, Fengli G. A study review of psychological status of health care professionals engaged in emerging acute respiratory infectious diseases. Chin Nurs Manag. 2019;19:83–86.
-
- World Health Organization. Available at: http://www.euro.who.int.influenza. Accessed March 12, 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

