High-Throughput Identification of MiR-145 Targets in Human Articular Chondrocytes
- PMID: 32403239
- PMCID: PMC7281014
- DOI: 10.3390/life10050058
High-Throughput Identification of MiR-145 Targets in Human Articular Chondrocytes
Abstract
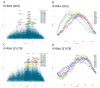
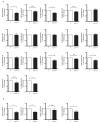
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play key roles in cartilage development and homeostasis and are dysregulated in osteoarthritis. MiR-145 modulation induces profound changes in the human articular chondrocyte (HAC) phenotype, partially through direct repression of SOX9. Since miRNAs can simultaneously silence multiple targets, we aimed to identify the whole targetome of miR-145 in HACs, critical if miR-145 is to be considered a target for cartilage repair. We performed RIP-seq (RNA-immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing) of miRISC (miRNA-induced silencing complex) in HACs overexpressing miR-145 to identify miR-145 direct targets and used cWords to assess enrichment of miR-145 seed matches in the identified targets. Further validations were performed by RT-qPCR, Western immunoblot, and luciferase assays. MiR-145 affects the expression of over 350 genes and directly targets more than 50 mRNAs through the 3'UTR or, more commonly, the coding region. MiR-145 targets DUSP6, involved in cartilage organization and development, at the translational level. DUSP6 depletion leads to MMP13 upregulation, suggesting a contribution towards the effect of miR-145 on MMP13 expression. In conclusion, miR-145 directly targets several genes involved in the expression of the extracellular matrix and inflammation in primary chondrocytes. Thus, we propose miR-145 as an important regulator of chondrocyte function and a new target for cartilage repair.
Keywords: RNA-immunoprecipitation; cartilage; chondrocyte; miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Billinghurst R.C., Dahlberg L., Ionescu M., Reiner A., Bourne R., Rorabeck C., Mitchell P., Hambor J., Diekmann O., Tschesche H., et al. Enhanced cleavage of type II collagen by collagenases in osteoarthritic articular cartilage. J. Clin. Investig. 1997;99:1534–1545. doi: 10.1172/JCI119316. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

