Circulating MicroRNAs as Potential Predictors of Anthracycline-Induced Troponin Elevation in Breast Cancer Patients: Diverging Effects of Doxorubicin and Epirubicin
- PMID: 32403263
- PMCID: PMC7290665
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9051418
Circulating MicroRNAs as Potential Predictors of Anthracycline-Induced Troponin Elevation in Breast Cancer Patients: Diverging Effects of Doxorubicin and Epirubicin
Abstract
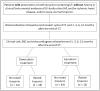
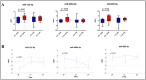
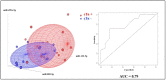
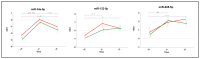
Anthracyclines are anti-neoplastic drugs presenting cardiotoxicity as a side effect. Cardiac troponins (cTn) and echocardiography are currently used to assess cardiac damage and dysfunction, but early biomarkers identifying patients in need of preventive treatments remain a partially met need. Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) represent good candidates, so we investigated their possible roles as predictors of troponin elevation upon anthracycline treatment. Eighty-eight female breast cancer patients administered with doxorubicin (DOX) or epirubicin (EPI) were divided into four groups basing on drug type and cTn positive (cTn+) or negative (cTn-) levels: DOX cTn-, DOX cTn+, EPI cTn- and EPI cTn+. Blood was collected at baseline, during treatment, and at follow-up. We identified plasma miRNAs of interest by OpenArray screening and single assay validation. Our results showed miR-122-5p, miR-499a-5p and miR-885-5p dysregulation in DOX patients at T0, identifying a signature separating, with good accuracy, DOX cTn- from DOX cTn+. No miRNAs showed differential expression in EPI subjects. Conversely, an anthracycline-mediated modulation (regardless of cTn) was observed for miR-34a-5p, -122-5p and -885-5p. Our study indicates specific circulating miRNAs as possible prediction markers for cardiac troponin perturbation upon anthracycline treatment. Indeed, our findings hint at the possible future use of plasma miRNAs to predict the cardiac responsiveness of patients to different anticancer agents.
Keywords: anthracyclines; biomarkers; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

