Search for ABCB1 Modulators Among 2-Amine-5-Arylideneimidazolones as a New Perspective to Overcome Cancer Multidrug Resistance
- PMID: 32403277
- PMCID: PMC7249047
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25092258
Search for ABCB1 Modulators Among 2-Amine-5-Arylideneimidazolones as a New Perspective to Overcome Cancer Multidrug Resistance
Abstract
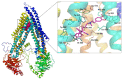
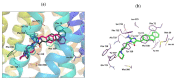
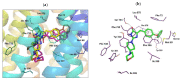
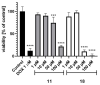
Multidrug resistance (MDR) is a severe problem in the treatment of cancer with overexpression of glycoprotein P (Pgp, ABCB1) as a reason for chemotherapy failure. A series of 14 novel 5-arylideneimidazolone derivatives containing the morpholine moiety, with respect to two different topologies (groups A and B), were designed and obtained in a three- or four-step synthesis, involving the Dimroth rearrangement. The new compounds were tested for their inhibition of the ABCB1 efflux pump in both sensitive (parental (PAR)) and ABCB1-overexpressing (MDR) T-lymphoma cancer cells in a rhodamine 123 accumulation assay. Their cytotoxic and antiproliferative effects were investigated by a thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. For active compounds, an insight into the mechanisms of action using either the luminescent Pgp-Glo™ Assay in vitro or docking studies to human Pgp was performed. The safety profile in vitro was examined. Structure-activity relationship (SAR) analysis was discussed. The most active compounds, representing both 2-substituted- (11) and Dimroth-rearranged 3-substituted (18) imidazolone topologies, displayed 1.38-1.46 fold stronger efflux pump inhibiting effects than reference verapamil and were significantly safer than doxorubicin in cell-based toxicity assays in the HEK-293 cell line. Results of mechanistic studies indicate that active imidazolones are substrates with increasing Pgp ATPase activity, and their dye-efflux inhibition via competitive action on the Pgp verapamil binding site was predicted in silico.
Keywords: 5-arylideneimidazolone; ABCB1 modulator; Dimroth rearrangement; Pgp; Pgp docking; T-lymphoma cancer cell; cancer MDR; rhodamine 123 accumulation assay.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Computer-Aided Search for 5-Arylideneimidazolone Anticancer Agents Able To Overcome ABCB1-Based Multidrug Resistance.ChemMedChem. 2021 Aug 5;16(15):2386-2401. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202100252. Epub 2021 Jun 7. ChemMedChem. 2021. PMID: 33929088
-
Reversal effect of FW-04-806, a macrolide dilactone compound, on multidrug resistance mediated by ABCB1 and ABCG2 in vitro and in vivo.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Sep 1;17(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0408-5. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 31472682 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of ABCB1 Transporter Confers Resistance to mTOR Inhibitor WYE-354 in Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 19;21(4):1387. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041387. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32092870 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of quinine on the multiple drug resistance and intracellular distribution of pirarubicin in LR73 tumor cells: a comparative study with verapamil and S9788 by confocal laser microspectrofluorometry].Bull Cancer. 1997 Apr;84(4):343-9. Bull Cancer. 1997. PMID: 9238156 Review. French.
-
Modulation and prevention of multidrug resistance by inhibitors of P-glycoprotein.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1997;40 Suppl:S13-9. doi: 10.1007/s002800051055. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9272128 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Insights into an Antibiotic Enhancer Action of New Morpholine-Containing 5-Arylideneimidazolones in the Fight against MDR Bacteria.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 19;22(4):2062. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042062. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669790 Free PMC article.
-
5-Arylidenerhodanines as P-gp Modulators: An Interesting Effect of the Carboxyl Group on ABCB1 Function in Multidrug-Resistant Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 16;23(18):10812. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810812. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142724 Free PMC article.
-
Chalcogen-Varied Imidazolone Derivatives as Antibiotic Resistance Breakers in Staphylococcus aureus Strains.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Nov 11;12(11):1618. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12111618. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998820 Free PMC article.
-
Enzyme-catalyzed synthesis of selenium-doped manganese phosphate for synergistic therapy of drug-resistant colorectal cancer.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Mar 1;21(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-01819-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 36859296 Free PMC article.
-
The pH-dependence of efflux ratios determined with bidirectional transport assays across cellular monolayers.Int J Pharm X. 2024 Jul 8;8:100269. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2024.100269. eCollection 2024 Dec. Int J Pharm X. 2024. PMID: 39669004 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

