Lymphatic and Immune Cell Cross-Talk Regulates Cardiac Recovery After Experimental Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 32404007
- PMCID: PMC7310303
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314370
Lymphatic and Immune Cell Cross-Talk Regulates Cardiac Recovery After Experimental Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
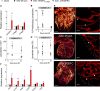
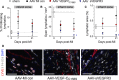
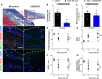
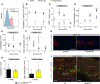
Objective: Lymphatics play an essential pathophysiological role in promoting fluid and immune cell tissue clearance. Conversely, immune cells may influence lymphatic function and remodeling. Recently, cardiac lymphangiogenesis has been proposed as a therapeutic target to prevent heart failure after myocardial infarction (MI). We investigated the effects of gene therapy to modulate cardiac lymphangiogenesis post-MI in rodents. Second, we determined the impact of cardiac-infiltrating T cells on lymphatic remodeling in the heart. Approach and Results: Comparing adenoviral versus adeno-associated viral gene delivery in mice, we found that only sustained VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor)-CC156S therapy, achieved by adeno-associated viral vectors, increased cardiac lymphangiogenesis, and led to reduced cardiac inflammation and dysfunction by 3 weeks post-MI. Conversely, inhibition of VEGF-C/-D signaling, through adeno-associated viral delivery of soluble VEGFR3 (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3), limited infarct lymphangiogenesis. Unexpectedly, this treatment improved cardiac function post-MI in both mice and rats, linked to reduced infarct thinning due to acute suppression of T-cell infiltration. Finally, using pharmacological, genetic, and antibody-mediated prevention of cardiac T-cell recruitment in mice, we discovered that both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells potently suppress, in part through interferon-γ, cardiac lymphangiogenesis post-MI.
Conclusions: We show that resolution of cardiac inflammation after MI may be accelerated by therapeutic lymphangiogenesis based on adeno-associated viral gene delivery of VEGF-CC156S. Conversely, our work uncovers a major negative role of cardiac-recruited T cells on lymphatic remodeling. Our results give new insight into the interconnection between immune cells and lymphatics in orchestration of cardiac repair after injury.
Keywords: heart failure; inflammation; interferon; lymphangiogenesis; macrophages.
Figures

Comment in
-
Soothing a Broken Heart: Can Therapeutic Cross-Talk Between Lymphatics and the Immune Response Improve Recovery From Myocardial Infarction?Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Jul;40(7):1611-1613. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314666. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32579475 No abstract available.
References
-
- Alitalo K, Tammela T, Petrova TV. Lymphangiogenesis in development and human disease. Nature. 2005;438:946–953. doi: 10.1038/nature04480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

