TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 promote SARS-CoV-2 infection of human small intestinal enterocytes
- PMID: 32404436
- PMCID: PMC7285829
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abc3582
TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4 promote SARS-CoV-2 infection of human small intestinal enterocytes
Abstract
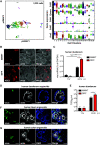
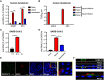
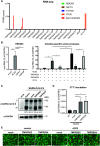
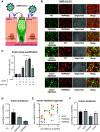
Gastrointestinal symptoms and fecal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 RNA are frequently observed in COVID-19 patients. However, it is unclear whether SARS-CoV-2 replicates in the human intestine and contributes to possible fecal-oral transmission. Here, we report productive infection of SARS-CoV-2 in ACE2+ mature enterocytes in human small intestinal enteroids. Expression of two mucosa-specific serine proteases, TMPRSS2 and TMPRSS4, facilitated SARS-CoV-2 spike fusogenic activity and promoted virus entry into host cells. We also demonstrate that viruses released into the intestinal lumen were inactivated by simulated human colonic fluid, and infectious virus was not recovered from the stool specimens of COVID-19 patients. Our results highlight the intestine as a potential site of SARS-CoV-2 replication, which may contribute to local and systemic illness and overall disease progression.
Copyright © 2020, The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures

References
-
- Wu F., Zhao S., Yu B., Chen Y.-M., Wang W., Song Z.-G., Hu Y., Tao Z.-W., Tian J.-H., Pei Y.-Y., Yuan M.-L., Zhang Y.-L., Dai F.-H., Liu Y., Wang Q.-M., Zheng J.-J., Xu L., Holmes E. C., Zhang Y.-Z., A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 579, 265–269 (2020). 10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou P., Yang X.-L., Wang X.-G., Hu B., Zhang L., Zhang W., Si H.-R., Zhu Y., Li B., Huang C.-L., Chen H.-D., Chen J., Luo Y., Guo H., Jiang R.-D., Liu M.-Q., Chen Y., Shen X.-R., Wang X., Zheng X.-S., Zhao K., Chen Q.-J., Deng F., Liu L.-L., Yan B., Zhan F.-X., Wang Y.-Y., Xiao G.-F., Shi Z.-L., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 579, 270–273 (2020). 10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann M., Kleine-Weber H., Schroeder S., Krüger N., Herrler T., Erichsen S., Schiergens T. S., Herrler G., Wu N.-H., Nitsche A., Müller M. A., Drosten C., Pöhlmann S., SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 181, 271–280.e8 (2020). 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 75N93019C00062/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AI135031/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AI135031/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AI138392/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 TR002344/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD020141/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI150796/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI059371/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR002346/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK109384/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI127828/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI125249/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI059371/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK052574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

