Whole genome sequence analysis of Cupriavidus campinensis S14E4C, a heavy metal resistant bacterium
- PMID: 32406019
- PMCID: PMC7239810
- DOI: 10.1007/s11033-020-05490-8
Whole genome sequence analysis of Cupriavidus campinensis S14E4C, a heavy metal resistant bacterium
Abstract
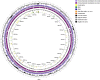
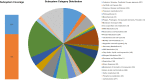
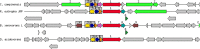
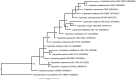
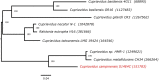
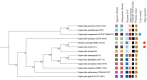
Cupriavidus sp. are model organisms for heavy metal(loid) resistance and aromatic compound's degradation studies and these characteristics make them a perfect candidate for biotechnological purposes. Bacterial strain S14E4C (identified as Cupriavidus campinensis) was isolated from a playground by enrichment method in a 0.25 mM containing medium. The analysis revealed that this bacterium is able to tolerate high concentrations of heavy metal(loid)s: Cd up to 19.5 mM, Pb to 9 mM, Hg to 5.5 mM and As to 2 mM in heavy metal(loid) salt containing nutrient medium. The whole genome data and analysis of the type strain of C. campinensis CCUG:44526T have not been available so far, thus here we present the genome sequencing results of strain S14E4C of the same species. Analysis was carried out to identify possible mechanisms for the heavy metal resistance and to map the genetic data of C. campinensis. The annotation pipelines revealed that the total genome of strain S14E4C is 6,375,175 bp length with a GC content of 66.3% and contains 2 plasmids with 295,460 bp (GC content 59.9%) and 50,483 bp (GC content 63%). In total 4460 coding sequences were assigned to known functions and 1508 to hypothetical proteins. Analysis proved that strain S14E4C is having gene clusters such as czc, mer, cus, chr, ars to encode various heavy metal resistance mechanisms that play an important role to survive in extreme environments.
Keywords: Cupriavidus campinensis; Heavy metal resistance; Whole genome sequence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ. Molecular, clinical and environmental toxicology: v.2: clinical toxicology. Choice Rev. 2013;47(10):5683.
-
- Goris J, et al. Classification of metal-resistant bacteria from industrial biotopes as Ralstonia campinensis sp. nov., Ralstonia metallidurans sp. nov. and Ralstonia basilensis Steinle et al. 1998 emend. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001;51(5):1773–1782. - PubMed
-
- Szuróczki S, et al. Arundinibacter roseus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Cytophagaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2019;69:2076–2081. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

