Improved velocity-selective-inversion arterial spin labeling for cerebral blood flow mapping with 3D acquisition
- PMID: 32406137
- PMCID: PMC7402012
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.28310
Improved velocity-selective-inversion arterial spin labeling for cerebral blood flow mapping with 3D acquisition
Abstract
Purpose: To further optimize the velocity-selective arterial spin labeling (VSASL) sequence utilizing a Fourier-transform based velocity-selective inversion (FT-VSI) pulse train, and to evaluate its utility for 3D mapping of cerebral blood flow (CBF) with a gradient- and spin-echo (GRASE) readout.
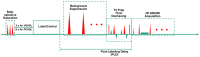
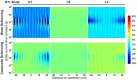
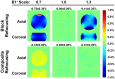
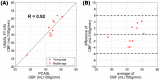
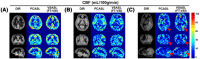
Methods: First, numerical simulations and phantom experiments were done to test the susceptibility to eddy currents and B1 field inhomogeneities for FT-VSI pulse trains with block and composite refocusing pulses. Second, the choices of the post-labeling delay (PLD) for FT-VSI prepared 3D VSASL were evaluated for the sensitivity to perfusion signal. The study was conducted among a young-age and a middle-age group at 3T. Both signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and CBF were quantitatively compared with pseudo-continuous ASL (PCASL). The optimized 3D VSI-ASL was also qualitatively compared with PCASL in a whole-brain coverage among two healthy volunteers and a brain tumor patient.
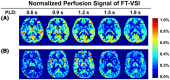
Results: The simulations and phantom test showed that composite refocusing pulses are more robust to both eddy-currents and B1 field inhomogeneities than block pulses. 3D VSASL images with FT-VSI preparation were acquired over a range of PLDs and PLD = 1.2 s was selected for its higher perfusion signal. FT-VSI labeling produced quantitative CBF maps with 27% higher SNR in gray matter compared to PCASL. 3D whole-brain CBF mapping using VSI-ASL were comparable to the corresponding PCASL results.
Conclusion: FT-VSI with 3D-GRASE readout was successfully implemented and showed higher sensitivity to perfusion signal than PCASL for both young and middle-aged healthy volunteers.
Keywords: 3D GRASE acquisition; arterial spin labeling; cerebral blood flow; velocity-selective inversion.
© 2020 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures


References
-
- Ye FQ, Frank JA, Weinberger DR, McLaughlin AC. Noise reduction in 3D perfusion imaging by attenuating the static signal in arterial spin tagging (ASSIST). Magn Reson Med. 2000;44:92‐100. - PubMed
-
- Alsop DC, Detre JA. Reduced transit‐time sensitivity in noninvasive magnetic resonance imaging of human cerebral blood flow. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1996;16:1236‐1249. - PubMed
-
- MacIntosh BJ, Filippini N, Chappell MA, Woolrich MW, Mackay CE, Jezzard P. Assessment of arterial arrival times derived from multiple inversion time pulsed arterial spin labeling MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2010;63:641‐647. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

