Long noncoding RNAs shape transcription in plants
- PMID: 32406332
- PMCID: PMC7714450
- DOI: 10.1080/21541264.2020.1764312
Long noncoding RNAs shape transcription in plants
Abstract
The advent of novel high-throughput sequencing techniques has revealed that eukaryotic genomes are massively transcribed although only a small fraction of RNAs exhibits protein-coding capacity. In the last years, long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have emerged as regulators of eukaryotic gene expression in a wide range of molecular mechanisms. Plant lncRNAs can be transcribed by alternative RNA polymerases, acting directly as long transcripts or can be processed into active small RNAs. Several lncRNAs have been recently shown to interact with chromatin, DNA or nuclear proteins to condition the epigenetic environment of target genes or modulate the activity of transcriptional complexes. In this review, we will summarize the recent discoveries about the actions of plant lncRNAs in the regulation of gene expression at the transcriptional level.
Keywords: Long noncoding RNAs; MEDIATOR; PRC1; PRC2; Pol II; Polycomb; alternative splicing; circRNAs; genome topology; inverted repeats; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures


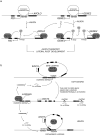
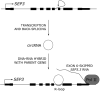
References
-
- Eddy SR. The C-value paradox, junk DNA and ENCODE. Curr Biol. 2012;22(21):R898–R899. - PubMed
-
- Thomas CA Jr. The genetic organization of chromosomes. Ann. Rev. Gen. 1971;5(1):237–256. - PubMed
-
- Ariel F, Romero-Barrios N, Jégu T, et al. Battles and hijacks: noncoding transcription in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2015;20(6):362–371. - PubMed
-
- Carninci P, Hayashizaki Y. Noncoding RNA transcription beyond annotated genes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007;17(2):139–144. - PubMed
-
- de Andres-pablo A, Morillon A, Wery M. LncRNAs, lost in translation or licence to regulate? Curr Genet. 2017;63(1):29–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
